Post by Infinity Blade on May 3, 2014 2:09:24 GMT 5
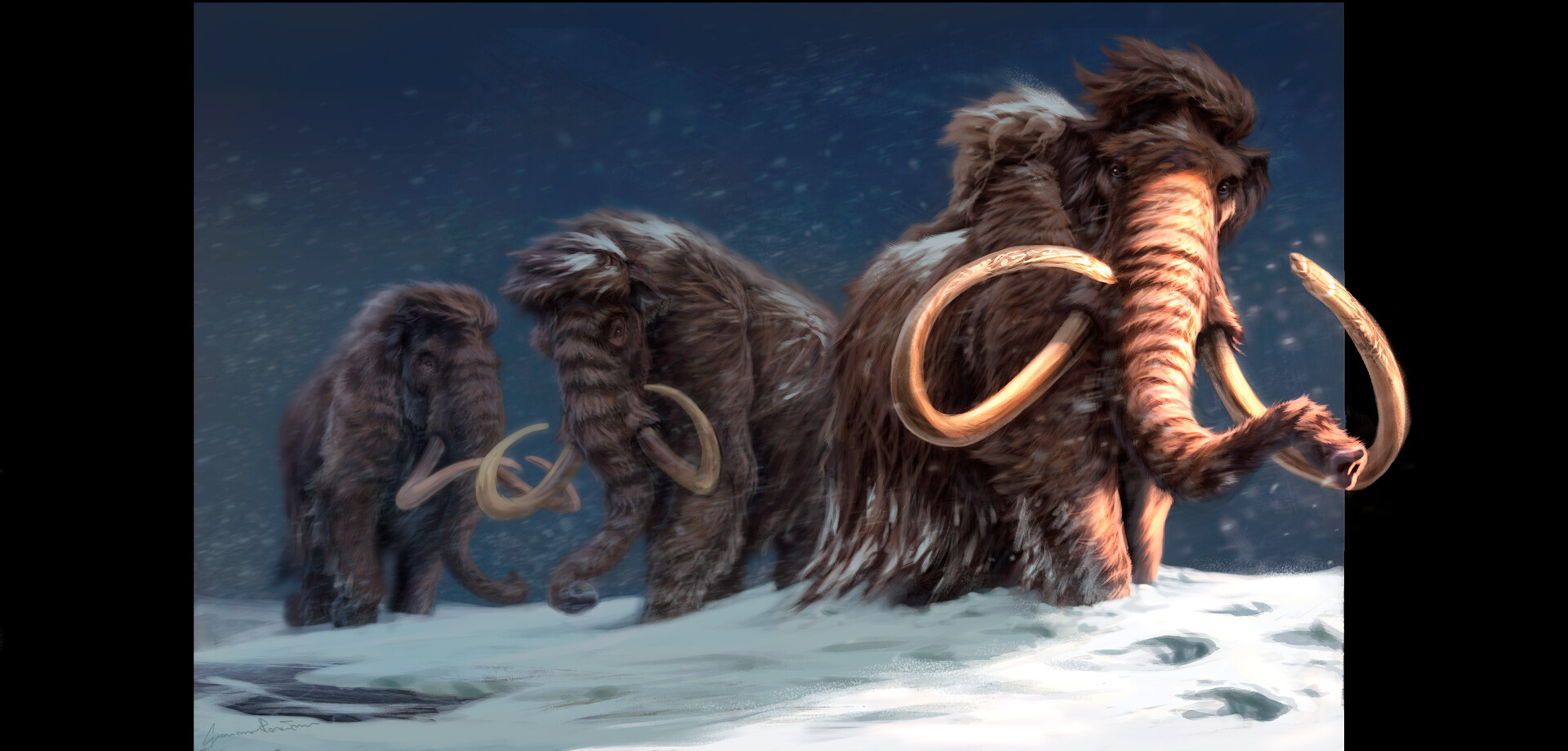
Woolly Mammoth-Mammuthus primigenius
The woolly mammoth (Mammuthus primigenius) was a species of mammoth, the common name for the extinct elephant genus Mammuthus. The woolly mammoth was one of the last in a line of mammoth species, beginning with Mammuthus subplanifrons in the early Pliocene. M. primigenius diverged from the steppe mammoth, M. trogontherii, about 200,000 years ago in eastern Asia. Its closest extant relative is the Asian elephant. The appearance and behaviour of this species are among the best studied of any prehistoric animal due to the discovery of frozen carcasses in Siberia and Alaska, as well as skeletons, teeth, stomach contents, dung, and depiction from life in prehistoric cave paintings. Mammoth remains had long been known in Asia before they became known to Europeans in the 17th century. The origin of these remains was long a matter of debate, and often explained as being remains of legendary creatures. The animal was only identified as an extinct species of elephant by Georges Cuvier in 1796. The woolly mammoth was roughly the same size as modern African elephants. Males reached shoulder heights between 2.7 and 3.4 m (9 and 11 ft) and weighed up to 6 tonnes (6.6 tons). Females averaged 2.6–2.9 metres (8.5–9.5 ft) in height. A newborn calf weighed about 90 kilograms (200 lb). The woolly mammoth was well adapted to the cold environment during the last ice age. It was covered in fur, with an outer covering of long guard hairs and a shorter undercoat. The colour of the coat varied from dark to light. The ears and tail were short to minimise frostbite and heat loss. It had long, curved tusks and four molars, which were replaced six times during the lifetime of an individual. Its behaviour was similar to that of modern elephants, and it used its tusks and trunk for manipulating objects, fighting, and foraging. The diet of the woolly mammoth was mainly grass and sedges. Specimens could probably reach the age of 60. Its habitat was the mammoth steppe, which stretched across northern Eurasia and North America.

© @ Graziano Roccatani
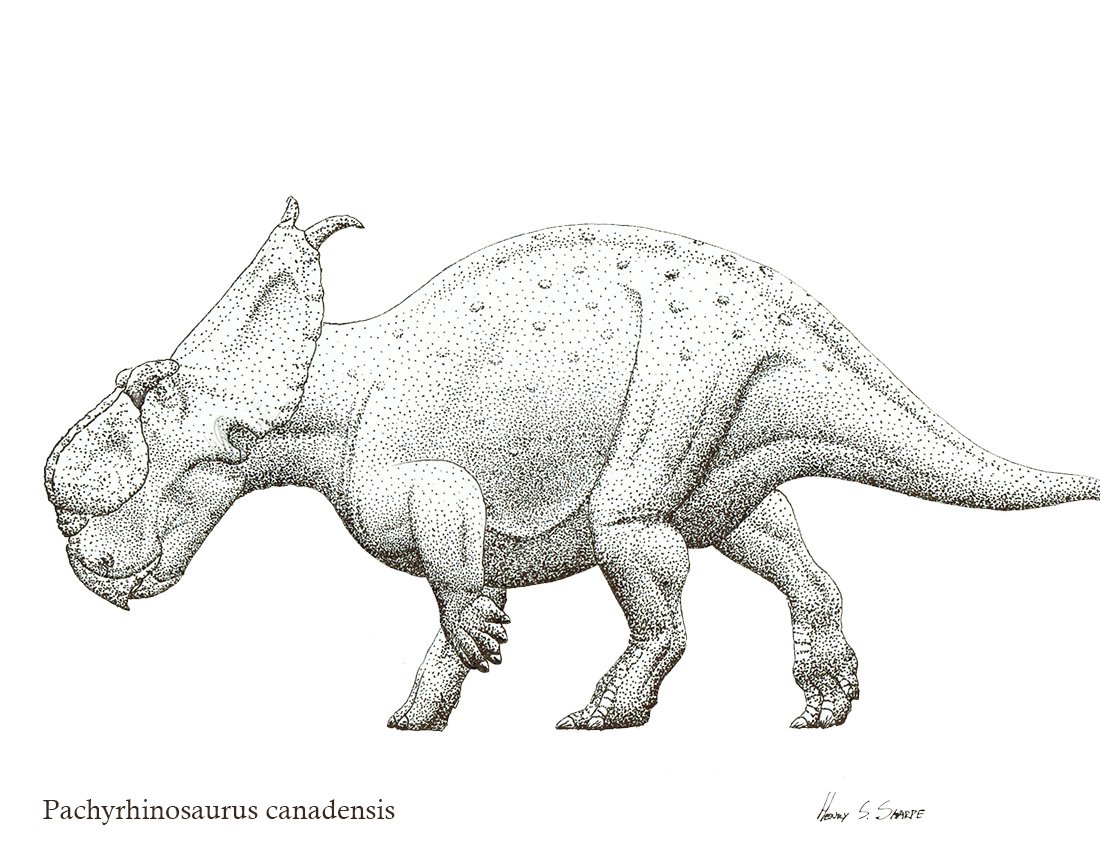
Pachyrhinosaurus canadensis
Pachyrhinosaurus (meaning "thick-nosed lizard") is an extinct genus of centrosaurine ceratopsid dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous period of North America. The first examples were discovered by Charles M. Sternberg in Alberta, Canada, in 1946, and named in 1950. Over a dozen partial skulls and a large assortment of other fossils from various species have been found in Alberta and Alaska. A great number were not available for study until the 1980s, resulting in a relatively recent increase of interest in the Pachyrhinosaurus. Three species have been identified. P. lakustai, from the Wapiti Formation, the bonebed horizon of which is roughly equivalent age to the upper Bearpaw and lower Horseshoe Canyon Formations, is known to have existed from about 73.5-72.5 million years ago. P. canadensis is younger, known only from the lower Horseshoe Canyon Formation, about 71.5-71 Ma ago. Fossils of the youngest species, P. perotorum, have been recovered from the Prince Creek Formation of Alaska, and date to 70-69 million years ago. The presence of three known species makes this genus the most speciose among the centrosaurines. A Pachyrhinosaurus was selected as the mascot for the 2010 Arctic Winter Games held in Grande Prairie, Alberta. The largest Pachyrhinosaurus species were 8 metres (26 ft) long. It weighed about four tons. They were herbivorous and possessed strong cheek teeth to help them chew tough, fibrous plants. Instead of horns, their skulls bore massive, flattened bosses; a large boss over the nose and a smaller one over the eyes. A prominent pair of horns grew from the frill and extended upwards. The skull also bore several smaller horns or ornaments that varied between individuals and between species. In P. canadensis and P. perotorum, the bosses over the nose and eyes nearly grew together, and were separated only by a narrow groove. In P. lakustai, the two bosses were separated by a wide gap. In P. canadensis and P. lakustai, the frill bore two additional small, curved, backward-pointed horns. These were not present in P. perotorum, and in fact some specimens of P. lakustai also lack them, which may indicate that the presence of these horns varied by age or sex. Various ornaments of the nasal boss have also been used to distinguish between different species of Pachyrhinosaurus. Both P. lakustai and P. perotorum bore a jagged, comb-like extension at the tip of the boss which was missing in P. canadensis. P. perotorum was unique in having a narrow dome in the middle of the back portion of the nasal boss, and P. lakustai had a pommel-like structure projecting from the front of the boss (the boss of P. canadensis was mainly flat on top and rounded). P. perotorum bore two unique, flattened horns which projected forward and down from the top edge of the frill, and P. lakustai bore another comb-like horn arising from the middle of the frill behind the eyes.
© @ Henry Sharpe
The woolly mammoth (Mammuthus primigenius) was a species of mammoth, the common name for the extinct elephant genus Mammuthus. The woolly mammoth was one of the last in a line of mammoth species, beginning with Mammuthus subplanifrons in the early Pliocene. M. primigenius diverged from the steppe mammoth, M. trogontherii, about 200,000 years ago in eastern Asia. Its closest extant relative is the Asian elephant. The appearance and behaviour of this species are among the best studied of any prehistoric animal due to the discovery of frozen carcasses in Siberia and Alaska, as well as skeletons, teeth, stomach contents, dung, and depiction from life in prehistoric cave paintings. Mammoth remains had long been known in Asia before they became known to Europeans in the 17th century. The origin of these remains was long a matter of debate, and often explained as being remains of legendary creatures. The animal was only identified as an extinct species of elephant by Georges Cuvier in 1796. The woolly mammoth was roughly the same size as modern African elephants. Males reached shoulder heights between 2.7 and 3.4 m (9 and 11 ft) and weighed up to 6 tonnes (6.6 tons). Females averaged 2.6–2.9 metres (8.5–9.5 ft) in height. A newborn calf weighed about 90 kilograms (200 lb). The woolly mammoth was well adapted to the cold environment during the last ice age. It was covered in fur, with an outer covering of long guard hairs and a shorter undercoat. The colour of the coat varied from dark to light. The ears and tail were short to minimise frostbite and heat loss. It had long, curved tusks and four molars, which were replaced six times during the lifetime of an individual. Its behaviour was similar to that of modern elephants, and it used its tusks and trunk for manipulating objects, fighting, and foraging. The diet of the woolly mammoth was mainly grass and sedges. Specimens could probably reach the age of 60. Its habitat was the mammoth steppe, which stretched across northern Eurasia and North America.

© @ Graziano Roccatani
Pachyrhinosaurus canadensis
Pachyrhinosaurus (meaning "thick-nosed lizard") is an extinct genus of centrosaurine ceratopsid dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous period of North America. The first examples were discovered by Charles M. Sternberg in Alberta, Canada, in 1946, and named in 1950. Over a dozen partial skulls and a large assortment of other fossils from various species have been found in Alberta and Alaska. A great number were not available for study until the 1980s, resulting in a relatively recent increase of interest in the Pachyrhinosaurus. Three species have been identified. P. lakustai, from the Wapiti Formation, the bonebed horizon of which is roughly equivalent age to the upper Bearpaw and lower Horseshoe Canyon Formations, is known to have existed from about 73.5-72.5 million years ago. P. canadensis is younger, known only from the lower Horseshoe Canyon Formation, about 71.5-71 Ma ago. Fossils of the youngest species, P. perotorum, have been recovered from the Prince Creek Formation of Alaska, and date to 70-69 million years ago. The presence of three known species makes this genus the most speciose among the centrosaurines. A Pachyrhinosaurus was selected as the mascot for the 2010 Arctic Winter Games held in Grande Prairie, Alberta. The largest Pachyrhinosaurus species were 8 metres (26 ft) long. It weighed about four tons. They were herbivorous and possessed strong cheek teeth to help them chew tough, fibrous plants. Instead of horns, their skulls bore massive, flattened bosses; a large boss over the nose and a smaller one over the eyes. A prominent pair of horns grew from the frill and extended upwards. The skull also bore several smaller horns or ornaments that varied between individuals and between species. In P. canadensis and P. perotorum, the bosses over the nose and eyes nearly grew together, and were separated only by a narrow groove. In P. lakustai, the two bosses were separated by a wide gap. In P. canadensis and P. lakustai, the frill bore two additional small, curved, backward-pointed horns. These were not present in P. perotorum, and in fact some specimens of P. lakustai also lack them, which may indicate that the presence of these horns varied by age or sex. Various ornaments of the nasal boss have also been used to distinguish between different species of Pachyrhinosaurus. Both P. lakustai and P. perotorum bore a jagged, comb-like extension at the tip of the boss which was missing in P. canadensis. P. perotorum was unique in having a narrow dome in the middle of the back portion of the nasal boss, and P. lakustai had a pommel-like structure projecting from the front of the boss (the boss of P. canadensis was mainly flat on top and rounded). P. perotorum bore two unique, flattened horns which projected forward and down from the top edge of the frill, and P. lakustai bore another comb-like horn arising from the middle of the frill behind the eyes.

© @ Henry Sharpe













