Post by dinosauria101 on Feb 2, 2019 22:44:19 GMT 5
Great White Shark - Carcharodon carcharias
The great white shark, scientific name Carcharodon carcharias, also known as the great white, white pointer, white shark, or white death, is a large lamniform shark found in coastal surface waters in all major oceans. It is known for its size, with the largest individuals known to have approached or exceeded 6 metres (20 ft) in length, and 2,268 kilograms (5,000 lb) in weight. This shark reaches maturity at around 15 years of age and can have a life span of over 30 years. The great white shark is arguably the world's largest known extant macropredatory fish and is one of the primary predators of marine mammals. Great whites display countershading, having a white underside and a grey dorsal area (sometimes in a brown or blue shade) that gives an overall mottled appearance. Great white sharks, like many other sharks, have rows of serrated teeth behind the main ones, ready to replace any that break off. When the shark bites it shakes its head side to side, helping the teeth saw off large chunks of flesh. Males reach maturity at 3.5–4.0 metres (11–13 ft) and females at 4.5–5.0 m (15–16 ft). Adults on average are 4–5.2 m (13–17.1 ft) long and have a mass of 680–1,100 kilograms (1,500–2,400 lb). Females are generally larger than males. It is widely accepted that the great white shark can reach 6.1 m (20 ft) in length and 1,900 kg (4,200 lb) in weight. The maximum size is subject to debate because some reports are rough estimations or speculations performed under questionable circumstances. Great white sharks are carnivorous and prey upon fish (e.g. tuna, rays, other sharks), cetaceans (i.e., dolphins, porpoises, whales), pinnipeds (e.g. seals, fur seals, and sea lions), sea turtles, sea otters, and seabirds. Great whites have also been known to eat objects that they are unable to digest.

Baryonyx walkeri
Baryonyx is a genus of theropod dinosaur which lived in the Barremian stage of the Early Cretaceous Period, about 130–125 million years ago. The first skeleton was discovered in 1983 in the Weald Clay Formation of Surrey, England, and became the holotype specimen of B. walkeri, named by palaeontologists Alan J. Charig and Angela C. Milner in 1986. The generic name, Baryonyx, means "heavy claw" and alludes to the animal's very large claw on the first finger; the specific name, walkeri, refers to its discoverer, amateur fossil collector William J. Walker. The holotype specimen is one of the most complete theropod skeletons from the UK (and remains the most complete spinosaurid), and its discovery attracted media attention. Specimens later discovered in other parts of the United Kingdom and Iberia have also been assigned to the genus. The holotype specimen, which may not have been fully grown, was estimated to have been between 7.5 and 10 m (25 and 33 ft) long and to have weighed between 1.2 and 1.7 t (1.3 and 1.9 short tons). Baryonyx had a long, low, and narrow snout, which has been compared to that of a gharial. The tip of the snout expanded to the sides in the shape of a rosette. Behind this, the upper jaw had a notch which fitted into the lower jaw (which curved upwards in the same area). It had a triangular crest on the top of its nasal bones. Baryonyx had a large number of finely serrated, conical teeth, with the largest teeth in front. The neck formed an S-shape, and the neural spines of its dorsal vertebrae increased in height from front to back. One elongated neural spine indicates it may have had a hump or ridge along the centre of its back. It had robust forelimbs, with the eponymous first-finger claw measuring about 31 cm (12 in) long. Baryonyx may have had semiaquatic habits, and coexisted with other theropod, ornithopod, and sauropod dinosaurs, as well as pterosaurs, crocodiles, turtles and fishes, in a fluvial environment.
Credit to Wikipedia
The great white shark, scientific name Carcharodon carcharias, also known as the great white, white pointer, white shark, or white death, is a large lamniform shark found in coastal surface waters in all major oceans. It is known for its size, with the largest individuals known to have approached or exceeded 6 metres (20 ft) in length, and 2,268 kilograms (5,000 lb) in weight. This shark reaches maturity at around 15 years of age and can have a life span of over 30 years. The great white shark is arguably the world's largest known extant macropredatory fish and is one of the primary predators of marine mammals. Great whites display countershading, having a white underside and a grey dorsal area (sometimes in a brown or blue shade) that gives an overall mottled appearance. Great white sharks, like many other sharks, have rows of serrated teeth behind the main ones, ready to replace any that break off. When the shark bites it shakes its head side to side, helping the teeth saw off large chunks of flesh. Males reach maturity at 3.5–4.0 metres (11–13 ft) and females at 4.5–5.0 m (15–16 ft). Adults on average are 4–5.2 m (13–17.1 ft) long and have a mass of 680–1,100 kilograms (1,500–2,400 lb). Females are generally larger than males. It is widely accepted that the great white shark can reach 6.1 m (20 ft) in length and 1,900 kg (4,200 lb) in weight. The maximum size is subject to debate because some reports are rough estimations or speculations performed under questionable circumstances. Great white sharks are carnivorous and prey upon fish (e.g. tuna, rays, other sharks), cetaceans (i.e., dolphins, porpoises, whales), pinnipeds (e.g. seals, fur seals, and sea lions), sea turtles, sea otters, and seabirds. Great whites have also been known to eat objects that they are unable to digest.

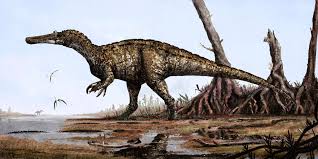
Baryonyx walkeri
Baryonyx is a genus of theropod dinosaur which lived in the Barremian stage of the Early Cretaceous Period, about 130–125 million years ago. The first skeleton was discovered in 1983 in the Weald Clay Formation of Surrey, England, and became the holotype specimen of B. walkeri, named by palaeontologists Alan J. Charig and Angela C. Milner in 1986. The generic name, Baryonyx, means "heavy claw" and alludes to the animal's very large claw on the first finger; the specific name, walkeri, refers to its discoverer, amateur fossil collector William J. Walker. The holotype specimen is one of the most complete theropod skeletons from the UK (and remains the most complete spinosaurid), and its discovery attracted media attention. Specimens later discovered in other parts of the United Kingdom and Iberia have also been assigned to the genus. The holotype specimen, which may not have been fully grown, was estimated to have been between 7.5 and 10 m (25 and 33 ft) long and to have weighed between 1.2 and 1.7 t (1.3 and 1.9 short tons). Baryonyx had a long, low, and narrow snout, which has been compared to that of a gharial. The tip of the snout expanded to the sides in the shape of a rosette. Behind this, the upper jaw had a notch which fitted into the lower jaw (which curved upwards in the same area). It had a triangular crest on the top of its nasal bones. Baryonyx had a large number of finely serrated, conical teeth, with the largest teeth in front. The neck formed an S-shape, and the neural spines of its dorsal vertebrae increased in height from front to back. One elongated neural spine indicates it may have had a hump or ridge along the centre of its back. It had robust forelimbs, with the eponymous first-finger claw measuring about 31 cm (12 in) long. Baryonyx may have had semiaquatic habits, and coexisted with other theropod, ornithopod, and sauropod dinosaurs, as well as pterosaurs, crocodiles, turtles and fishes, in a fluvial environment.
Credit to Wikipedia





