Post by rock on Apr 23, 2019 18:47:51 GMT 5
Amphicyon ingens
Neither bear nor dog, these extinct animals evolved to be massive predators.
Credit: Public domain
The bear dog, also called Amphicyon, shared features of bears (heavy-bodied, with feet planted flat on the ground) and dogs (relatively long legs and long snout), but they are neither bears (family Ursidae) nor dogs (family Canidae).
They were not specifically in the bear's or dog's scientific families, but they are classified in the Caniformia, or "dog-like" suborder. Modern animals in the Caniformia suborder include wolves, foxes, dogs, bears, sea lions and weasels. This makes bear dogs something like cousins to their namesakes. Also, these bear dogs should not be confused with the modern dog breed, the Karelian bear dog.
There were two main types of bear dogs. Some, like Borocyon robustum, had long limbs that were ideal for running and looked much like modern wolves. Others, such as Amphicyon longiramus, were stocky and looked more like modern bears, according to the Florida Museum of Natural History. MORE
Neither bear nor dog, these extinct animals evolved to be massive predators.
Credit: Public domain
The bear dog, also called Amphicyon, shared features of bears (heavy-bodied, with feet planted flat on the ground) and dogs (relatively long legs and long snout), but they are neither bears (family Ursidae) nor dogs (family Canidae).
They were not specifically in the bear's or dog's scientific families, but they are classified in the Caniformia, or "dog-like" suborder. Modern animals in the Caniformia suborder include wolves, foxes, dogs, bears, sea lions and weasels. This makes bear dogs something like cousins to their namesakes. Also, these bear dogs should not be confused with the modern dog breed, the Karelian bear dog.
There were two main types of bear dogs. Some, like Borocyon robustum, had long limbs that were ideal for running and looked much like modern wolves. Others, such as Amphicyon longiramus, were stocky and looked more like modern bears, according to the Florida Museum of Natural History.
Much like dogs and bears of today, bear dogs had a range of sizes. They could weigh just few pounds or grow to over 1,000 lbs. (450 kilograms). It is thought that the early evolutions of the bear dog were very small, around Chihuahua size. As they continued to evolve, they seemed to have become progressively larger, according to The Field Museum.
Evolving into bigger animals has several advantages and disadvantages. While becoming bigger would have enabled them to take down bigger prey and be higher on the food chain, they also would have required more food and reproduced more slowly.
"Their massiveness suggest that they could prey upon many kinds of mammals and other animals. Fortunately, they were extinct before humans appeared on the scene," said Wilkins.

Copyright @ DeviantArt user Leogon
Polar bear (Ursus maritimus)
Polar bears live in the Arctic.
Polar bears have black skin and although their fur appears white, it is actually transparent.
It is the largest carnivore (meat eater) that lives on land.
Polar bears use sea ice as a platform to hunt seals.
Seals make up most of a polar bears diet.
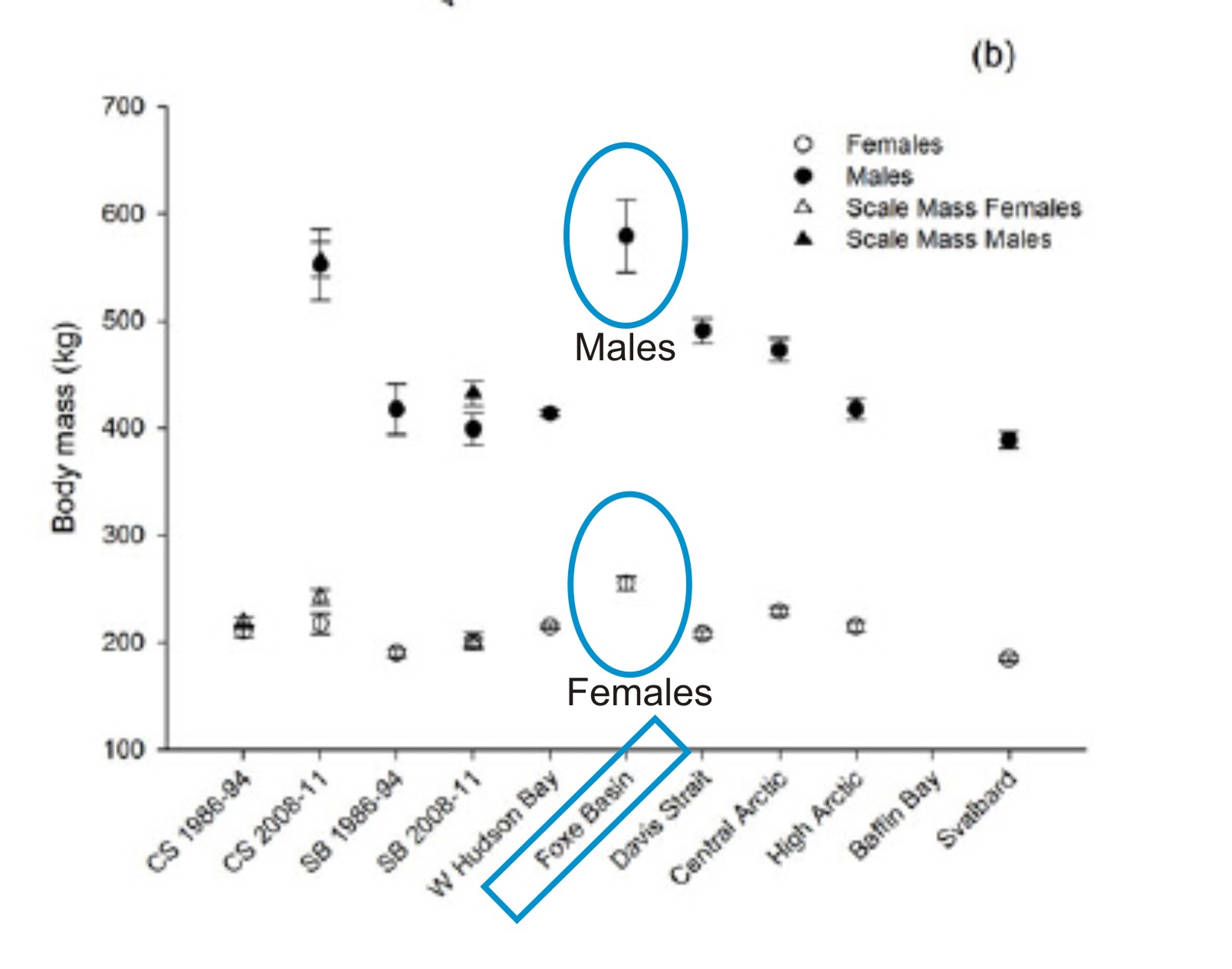
Male polar bears can weigh up to 680 kg (1500 lb).
Female polar bears usually only weigh about half as much as males.
Polar bears spend most of their time at sea.
Scientists estimate that there are around 20000 polar bears.
Polar bears have 42 teeth.
The scientific name for the polar bear is ‘ursus maritimus’.
Polar bears keep warm thanks to nearly 10 cm of blubber under the skin.
Polar bears have an excellent sense of smell, with the ability to detect seals nearly a mile away (1.6 km).
Polar bears can reach speeds up to 40 kph (25 mph) on land and 10 kph (6 mph) in water.
The polar bear was the mascot for the 1988 Winter Olympics in Calgary, Canada.

Neither bear nor dog, these extinct animals evolved to be massive predators.
Credit: Public domain
The bear dog, also called Amphicyon, shared features of bears (heavy-bodied, with feet planted flat on the ground) and dogs (relatively long legs and long snout), but they are neither bears (family Ursidae) nor dogs (family Canidae).
They were not specifically in the bear's or dog's scientific families, but they are classified in the Caniformia, or "dog-like" suborder. Modern animals in the Caniformia suborder include wolves, foxes, dogs, bears, sea lions and weasels. This makes bear dogs something like cousins to their namesakes. Also, these bear dogs should not be confused with the modern dog breed, the Karelian bear dog.
There were two main types of bear dogs. Some, like Borocyon robustum, had long limbs that were ideal for running and looked much like modern wolves. Others, such as Amphicyon longiramus, were stocky and looked more like modern bears, according to the Florida Museum of Natural History. MORE
Neither bear nor dog, these extinct animals evolved to be massive predators.
Credit: Public domain
The bear dog, also called Amphicyon, shared features of bears (heavy-bodied, with feet planted flat on the ground) and dogs (relatively long legs and long snout), but they are neither bears (family Ursidae) nor dogs (family Canidae).
They were not specifically in the bear's or dog's scientific families, but they are classified in the Caniformia, or "dog-like" suborder. Modern animals in the Caniformia suborder include wolves, foxes, dogs, bears, sea lions and weasels. This makes bear dogs something like cousins to their namesakes. Also, these bear dogs should not be confused with the modern dog breed, the Karelian bear dog.
There were two main types of bear dogs. Some, like Borocyon robustum, had long limbs that were ideal for running and looked much like modern wolves. Others, such as Amphicyon longiramus, were stocky and looked more like modern bears, according to the Florida Museum of Natural History.
Much like dogs and bears of today, bear dogs had a range of sizes. They could weigh just few pounds or grow to over 1,000 lbs. (450 kilograms). It is thought that the early evolutions of the bear dog were very small, around Chihuahua size. As they continued to evolve, they seemed to have become progressively larger, according to The Field Museum.
Evolving into bigger animals has several advantages and disadvantages. While becoming bigger would have enabled them to take down bigger prey and be higher on the food chain, they also would have required more food and reproduced more slowly.
"Their massiveness suggest that they could prey upon many kinds of mammals and other animals. Fortunately, they were extinct before humans appeared on the scene," said Wilkins.

Copyright @ DeviantArt user Leogon
Polar bear (Ursus maritimus)
Polar bears live in the Arctic.
Polar bears have black skin and although their fur appears white, it is actually transparent.
It is the largest carnivore (meat eater) that lives on land.
Polar bears use sea ice as a platform to hunt seals.
Seals make up most of a polar bears diet.
Male polar bears can weigh up to 680 kg (1500 lb).
Female polar bears usually only weigh about half as much as males.
Polar bears spend most of their time at sea.
Scientists estimate that there are around 20000 polar bears.
Polar bears have 42 teeth.
The scientific name for the polar bear is ‘ursus maritimus’.
Polar bears keep warm thanks to nearly 10 cm of blubber under the skin.
Polar bears have an excellent sense of smell, with the ability to detect seals nearly a mile away (1.6 km).
Polar bears can reach speeds up to 40 kph (25 mph) on land and 10 kph (6 mph) in water.
The polar bear was the mascot for the 1988 Winter Olympics in Calgary, Canada.