Post by dinosauria101 on Jun 1, 2019 16:09:09 GMT 5
Siats meekerorum
Siats is an extinct genus of large neovenatorid theropod dinosaur known from the Late Cretaceous Cedar Mountain Formation of Utah, USA. It contains a single species, Siats meekerorum. S. meekerorum is the first neovenatorid discovered in North America and represents the geologically youngest allosauroid yet discovered from the continent. The holotype came from a single immature individual, based on its incompletely fused neural arches to their centra in the vertebral column. The taxon is characterized by seven diagnostic (including four autapomorphies) features which include the broad neural spines on the dorsal vertebrae and the subtriangular crosssection of the distal caudal vertebrae, with the latter being an autapomorphy. The discovery of this neovenatorid also reveals that tyrannosauroids did not begin to dominate North America until the late cretaceous due to the presence of allosauroids such as Siats. Siats represents the third largest theropod from North America, after Acrocanthosaurus and Tyrannosaurus. Weight?? "At 24 feet (7.3 meters) long and weighing about 2.5 tons, the 80-million-year-old Lythronax (pronounced LYE-thro-nax) lacked the even-more-massive size of T. rex, says the University of Utah's Mark Loewen, who headed the team reporting the dinosaur's discovery in PLOS One." A adult would have presumably been larger.
NOTE: Siats was probably a tyrannosauroid instead of an allosauroid, and would've likely weighed about 6 tons as an adult

Dacentrurus armatus
Dacentrurus (meaning "tail full of points"), originally known as Omosaurus, was a large stegosaur of the Late Jurassic Period (154 - 150 mya) of Europe. Its type species, Omosaurus armatus, was named in 1875, based on a skeleton found in the Kimmeridge Clay of England. In 1902 the genus was renamed Dacentrurus because the name Omosaurus had already been used for a crocodylian. After 1875, half a dozen other species would be named but perhaps only Dacentrurus armatus is valid. Finds of this animal have been limited and much of its appearance is uncertain. It was a heavily built quadrupedal herbivore, adorned with plates and spikes. Dacentrurus was a large stegosaurid. Some specimens reached lengths 10 meters (33 ft) and weighed 8 t (8.8 short tons). Many books claim that Dacentrurus was a small stegosaur, when in fact finds such as a 1.5 metres (4.9 ft) wide pelvis indicate that Dacentrurus was among the largest of them. For a stegosaur the gut was especially broad, and a massive rump is also indicated by exceptionally wide dorsal vertebrae centra. The hindlimb was rather short, but the forelimb relatively long, largely because of a long lower arm. Although Dacentrurus is considered to have the same proportions as Stegosaurus, its plate and spike configuration is known to be rather different, as it probably had both two rows of small plates on its neck and two rows of longer spikes along its tail. The holotype specimen of Dacentrurus armatus contained a small blunt asymmetrical neck plate and also included a tail spike which could have been part of a thagomizer. The tail spike had sharp cutting edges on its front and rear side. Dacentrurus has sometimes been portrayed with a spike growing near the shoulder, similarly to a Kentrosaurus. Whether this portrayal is accurate or not is not yet determined.
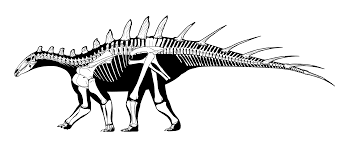
Credit to Wikipedia
Siats is an extinct genus of large neovenatorid theropod dinosaur known from the Late Cretaceous Cedar Mountain Formation of Utah, USA. It contains a single species, Siats meekerorum. S. meekerorum is the first neovenatorid discovered in North America and represents the geologically youngest allosauroid yet discovered from the continent. The holotype came from a single immature individual, based on its incompletely fused neural arches to their centra in the vertebral column. The taxon is characterized by seven diagnostic (including four autapomorphies) features which include the broad neural spines on the dorsal vertebrae and the subtriangular crosssection of the distal caudal vertebrae, with the latter being an autapomorphy. The discovery of this neovenatorid also reveals that tyrannosauroids did not begin to dominate North America until the late cretaceous due to the presence of allosauroids such as Siats. Siats represents the third largest theropod from North America, after Acrocanthosaurus and Tyrannosaurus. Weight?? "At 24 feet (7.3 meters) long and weighing about 2.5 tons, the 80-million-year-old Lythronax (pronounced LYE-thro-nax) lacked the even-more-massive size of T. rex, says the University of Utah's Mark Loewen, who headed the team reporting the dinosaur's discovery in PLOS One." A adult would have presumably been larger.
NOTE: Siats was probably a tyrannosauroid instead of an allosauroid, and would've likely weighed about 6 tons as an adult

Dacentrurus armatus
Dacentrurus (meaning "tail full of points"), originally known as Omosaurus, was a large stegosaur of the Late Jurassic Period (154 - 150 mya) of Europe. Its type species, Omosaurus armatus, was named in 1875, based on a skeleton found in the Kimmeridge Clay of England. In 1902 the genus was renamed Dacentrurus because the name Omosaurus had already been used for a crocodylian. After 1875, half a dozen other species would be named but perhaps only Dacentrurus armatus is valid. Finds of this animal have been limited and much of its appearance is uncertain. It was a heavily built quadrupedal herbivore, adorned with plates and spikes. Dacentrurus was a large stegosaurid. Some specimens reached lengths 10 meters (33 ft) and weighed 8 t (8.8 short tons). Many books claim that Dacentrurus was a small stegosaur, when in fact finds such as a 1.5 metres (4.9 ft) wide pelvis indicate that Dacentrurus was among the largest of them. For a stegosaur the gut was especially broad, and a massive rump is also indicated by exceptionally wide dorsal vertebrae centra. The hindlimb was rather short, but the forelimb relatively long, largely because of a long lower arm. Although Dacentrurus is considered to have the same proportions as Stegosaurus, its plate and spike configuration is known to be rather different, as it probably had both two rows of small plates on its neck and two rows of longer spikes along its tail. The holotype specimen of Dacentrurus armatus contained a small blunt asymmetrical neck plate and also included a tail spike which could have been part of a thagomizer. The tail spike had sharp cutting edges on its front and rear side. Dacentrurus has sometimes been portrayed with a spike growing near the shoulder, similarly to a Kentrosaurus. Whether this portrayal is accurate or not is not yet determined.
Credit to Wikipedia




