Post by Ceratodromeus on May 15, 2015 1:18:49 GMT 5

Scientific classification
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Class: Reptilia
Order: Squamata
Suborder: Serpentes
Family: Viperidae
Subfamily: Viperinae
Genus: Bitis
Species: Bitis gabonica
Description: The Gaboon viper is a very heavily built snake, with males averaging a total length of 5ft(1.5m)and females averaging a total length of 5.5ft( 1.6m). Sexual dimorphism is present, with the females being larger.{1} These snakes can weigh upwards of 10kg(22lbs){2}, but typically are much smaller then that. Their dull colorations( a mixture of browns, grays, whites, and yellows) helps them blend in with the forest floor, where they spend the vast majority of their time. This snake is Solenoglyphic, a feature unique in Vipers. B. gabonica has the longest fangs of any known venomous snake, measuing up to 2in(5cm).

They are also one of the fastest striking venomous snakes
| Species | m s-1 | km h -1 | duration (ms) |
| V. ammodytes | 1.32 | 46.8 | 300 |
| B. nasicornis | 0.39 | 14.0 | 220 |
| B.gabonica | 1.55 | 55.8 | 277.5 |
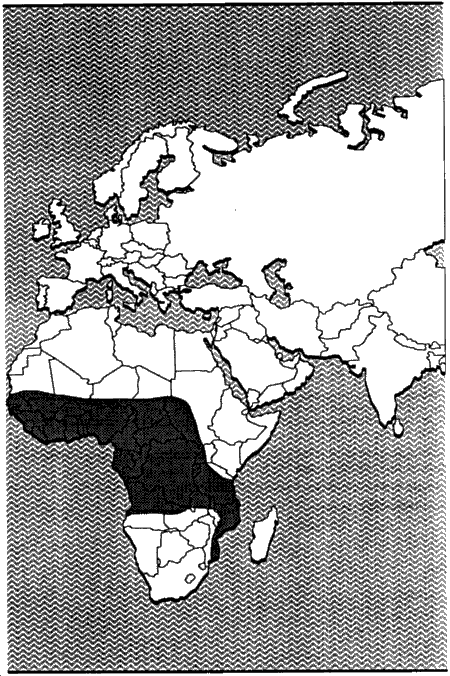
Geographic range: These snakes can be found throughout Sub-Saharan Africa
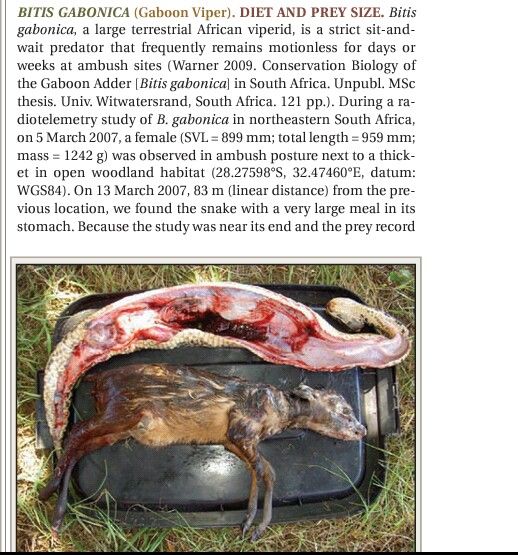
Dietary habits: Like other vipers, this snake primarily feeds on small mammals. Rodents(Mus) were preffered over shrews(Sp.). B. gabonica is also noted to have taken reptiles (M. fernandii, Trachylepis sp), though this trend was seen more often in juvenile snakes rather then adults.{1} Other noted prey items include birds, porcupines, and (at least attempted) primates.{5} Though sympatric with the closely related B. nasicornis, their dietary habits are completely different. Thus, they avoid extensive competition.
Reproduction: These snakes are viviparous(live bearing). Breeding occurs from September to December with the young being born in May or June of next year. They are already rather large, measuring ~30cm(11.8in){6} The mother does not watch over the; as soon as they hatch they're on their own.
References:
{1}Luiselli, Luca, and Godfrey C. Akani. "Diet of sympatric Gaboon Vipers (Bitis gabonica) and Nose‐horned Vipers (Bitis nasicornis) in southern Nigeria." African Journal of Herpetology 52.2 (2003): 101-106.
{2}Bonnet, Xavier, et al. "Plastic vipers: influence of food intake on the size and shape of Gaboon vipers (Bitis gabonica)." Journal of Zoology 255.3 (2001): 341-351.
{3}Amphibia-Reptilia 13 (1992): 315-325, E. J. Brill, Leiden. High speed motion analysis of the predatory strike and fluorographic study of oesophageal deglutition in Vípera ammodytes: more than meets the eye. Anwar Janoo, Jean-Pierre Gase
{4}Duarte, Marcelo Ribeiro. "Prickly food: snakes preying upon porcupines." Phyllomedusa: Journal of Herpetology 2.2 (2003): 109-112.
{5}Foerster, Steffen. "Two incidents of venomous snakebite on juvenile blue and Sykes monkeys (Cercopithecus mitis stuhlmanni and C. m. albogularis)." Primates 49.4 (2008): 300-303.
{6} Luiselli, Luca, et al. "Reproductive strategies of sympatric Bitis gabonica and Bitis nasicornis (Viperidae) in the Niger Delta (Port Harcourt, Nigeria): preliminary data." Amphibia-Reptilia 19.2 (1998): 223-229.