Post by dinosauria101 on Feb 21, 2019 2:29:25 GMT 5
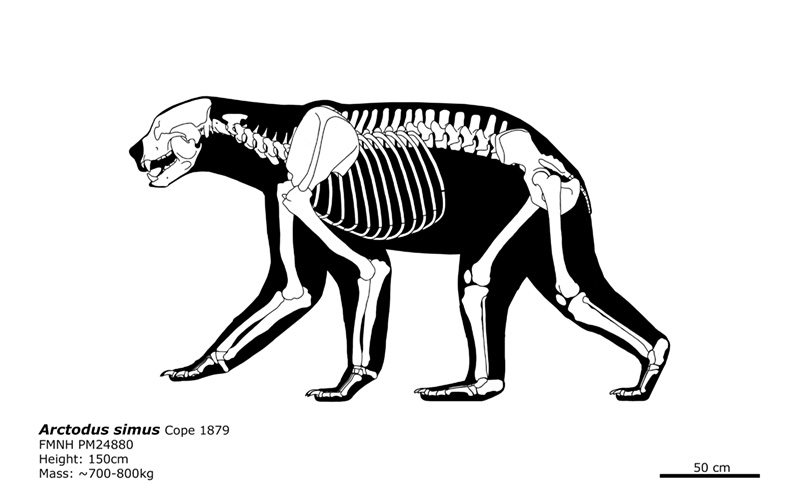
Agriotherium africanum
Agriotherium is an extinct genus of bears whose fossils are found Miocene through Pleistocene-aged strata of North America, Europe, Africa, and Asia, living from ~13.6–2.5 Ma, existing for approximately 11.1 million years. Materials of the late surviving A. africanum from Africa has suggested that A. africanum died out soon during the early Gelasian. Agriotherium was about 2.7 metres (9 ft) in body length and weighed around 900 kilograms (1,980 lb), making it larger than most living bears. Except for the extinct subspecies of the modern polar bear Ursus maritimus tyrannus and Arctotherium, Agriotherium was, along with the short-faced bear, Arctodus simus, the largest member of terrestrial Carnivora. It had dog-like crushing teeth. A 2011 estimate that compared the bites of a few selected bears, both extant and extinct, concluded that Agriotherium had the strongest bite-force of any mammalian land-predator yet estimated. It was an omnivore, feeding on camelids, horses, rhinos, bovids, chalicotheres and small or young proboscideans as well as vegetation. Agriotherium also likely scavenged, and would not have been hesitant about stealing kills from such animals as the sabertooth cat Amphimachairodus, with whom it shared territory in both China and North America, and the feliform Barbourofelis, which it lived alongside in Texas, as evidenced by fossil deposits at Coffee Ranch.

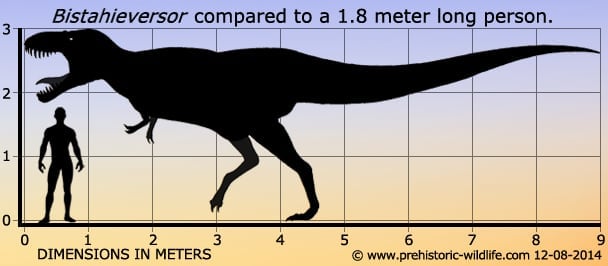
Bistahieversor sealeyi
Bistahieversor (meaning "Bistahi destroyer") is a genus of tyrannosaurid dinosaur. Bistahieversor existed in the Late Cretaceous Hunter Wash member of the Kirtland Formation, which has been dated to 74.55 ± 0.29 Ma. The name Bistahieversor comes from the Navajo Bistahí, or "place of the adobe formations" in reference to the Bisti/De-Na-Zin Wilderness where it was found, and eversor, meaning "destroyer. Material from both adolescent and adult individuals has been found in the Kirtland Formation of New Mexico, United States. Adult Bistahieversor are estimated to have been around 9 meters (30 ft) long, weighing at least a ton. The snout is deep, indicating that the feature is not unique to more derived tyrannosaurs such as Tyrannosaurus. Geographical barriers such as the newly forming Rocky Mountains may have isolated the more southerly Bistahieversor from more derived northern tyrannosaurs. The first remains now attributed to Bistahieversor, a partial skull and skeleton, were described in 1990 as a specimen of Aublysodon. Additional remains, consisting of the incomplete skull and skeleton of a juvenile, were described in 1992. Bistahieversor is a genus of derived dinosaur currently classified in the subfamily Tyrannosaurinae. It is more derived than Teratophoneus but less derived than Lythronax. It forms the sister taxon of a group including Lythronax, Nanuqsaurus, Tyrannosaurus, Tarbosaurus and Zhuchengtyrannus.
Credit to Wikipedia
Agriotherium is an extinct genus of bears whose fossils are found Miocene through Pleistocene-aged strata of North America, Europe, Africa, and Asia, living from ~13.6–2.5 Ma, existing for approximately 11.1 million years. Materials of the late surviving A. africanum from Africa has suggested that A. africanum died out soon during the early Gelasian. Agriotherium was about 2.7 metres (9 ft) in body length and weighed around 900 kilograms (1,980 lb), making it larger than most living bears. Except for the extinct subspecies of the modern polar bear Ursus maritimus tyrannus and Arctotherium, Agriotherium was, along with the short-faced bear, Arctodus simus, the largest member of terrestrial Carnivora. It had dog-like crushing teeth. A 2011 estimate that compared the bites of a few selected bears, both extant and extinct, concluded that Agriotherium had the strongest bite-force of any mammalian land-predator yet estimated. It was an omnivore, feeding on camelids, horses, rhinos, bovids, chalicotheres and small or young proboscideans as well as vegetation. Agriotherium also likely scavenged, and would not have been hesitant about stealing kills from such animals as the sabertooth cat Amphimachairodus, with whom it shared territory in both China and North America, and the feliform Barbourofelis, which it lived alongside in Texas, as evidenced by fossil deposits at Coffee Ranch.

Bistahieversor sealeyi
Bistahieversor (meaning "Bistahi destroyer") is a genus of tyrannosaurid dinosaur. Bistahieversor existed in the Late Cretaceous Hunter Wash member of the Kirtland Formation, which has been dated to 74.55 ± 0.29 Ma. The name Bistahieversor comes from the Navajo Bistahí, or "place of the adobe formations" in reference to the Bisti/De-Na-Zin Wilderness where it was found, and eversor, meaning "destroyer. Material from both adolescent and adult individuals has been found in the Kirtland Formation of New Mexico, United States. Adult Bistahieversor are estimated to have been around 9 meters (30 ft) long, weighing at least a ton. The snout is deep, indicating that the feature is not unique to more derived tyrannosaurs such as Tyrannosaurus. Geographical barriers such as the newly forming Rocky Mountains may have isolated the more southerly Bistahieversor from more derived northern tyrannosaurs. The first remains now attributed to Bistahieversor, a partial skull and skeleton, were described in 1990 as a specimen of Aublysodon. Additional remains, consisting of the incomplete skull and skeleton of a juvenile, were described in 1992. Bistahieversor is a genus of derived dinosaur currently classified in the subfamily Tyrannosaurinae. It is more derived than Teratophoneus but less derived than Lythronax. It forms the sister taxon of a group including Lythronax, Nanuqsaurus, Tyrannosaurus, Tarbosaurus and Zhuchengtyrannus.

Credit to Wikipedia