Post by dinosauria101 on Feb 26, 2019 18:26:18 GMT 5
Elasmotherium sibiricum
Elasmotherium ("thin plate beast") is an extinct genus of large rhinoceros endemic to Eurasia during the Late Pliocene through the Pleistocene, existing from 2.6 Ma to at least as late as 39,000 years ago in the Late Pleistocene. E. sibiricum, was the size of a mammoth and is thought to have borne a large, thick horn on its forehead. Theories about the function of this horn include defence, attracting mates, driving away competitors, sweeping snow from the grass in winter and digging for water and plant roots. Like all rhinoceroses, elasmotheres were herbivorous. Unlike any others, its high-crowned molars were ever-growing. Its legs were longer than those of other rhinos and were adapted for galloping, giving it a horse-like gait. The known specimens of E. sibiricum reach up to 4.5 m (15 ft) in body length with shoulder heights over 2 m (6 ft 7 in). Elasmotherium weighed 4.5-5 ton.

Mapusaurus roseae
Mapusaurus ("Earth lizard") was a giant carnosaurian, Carcharodontosaurid dinosaur from the early Late Cretaceous (late Cenomanian to early Turonian stage) of what is now Argentina and possibly Chile. It was roughly similar in size to its close relative Giganotosaurus, averaging about 12.4 meters and 7 tons and getting to 13.6 meters long and 8.5 tons at maximum. The longest individual for which Coria and Currie (2006) provided a concrete estimate in Table 1 (apendix lll) is the animal to which femur MCF-PVPH-208.203 belonged; this individual is estimated as 10.2 metres (33 ft) long, but it is a juvenile. The fossil remains of Mapusaurus were discovered in a bone bed containing at least seven individuals of various growth stages. Coria and Currie speculated that this may represent a long term, possibly coincidental accumulation of carcasses (some sort of predator trap) and may provide clues about Mapusaurus behavior. Other known theropod bone beds include the Allosaurus-dominated Cleveland-Lloyd Dinosaur Quarry of Utah, an Albertosaurus bone bed from Alberta and a Daspletosaurus bone bed from Montana. Paleontologist Rodolfo Coria, of the Museo Carmen Funes, contrary to his published article, repeated in a press-conference earlier suggestions that this congregation of fossil bones may indicate that Mapusaurus hunted in groups and worked together to take down large prey, such as the immense sauropod Argentinosaurus. If so, this would be the first substantive evidence of gregarious behavior by large theropods other than Tyrannosaurus, although whether they might have hunted in organized packs (as wolves do) or simply attacked in a mob, is unknown.
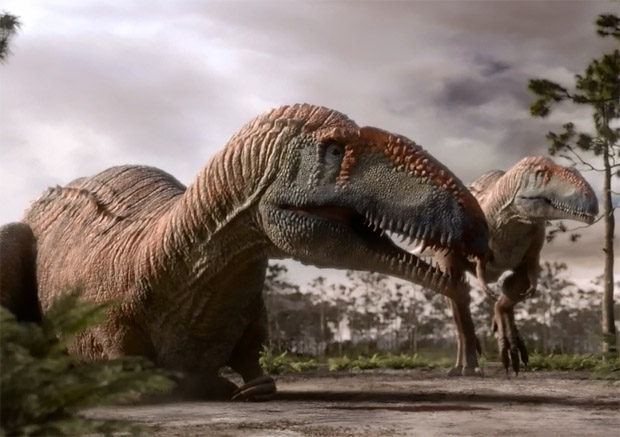
Credit to Wikipedia
Elasmotherium ("thin plate beast") is an extinct genus of large rhinoceros endemic to Eurasia during the Late Pliocene through the Pleistocene, existing from 2.6 Ma to at least as late as 39,000 years ago in the Late Pleistocene. E. sibiricum, was the size of a mammoth and is thought to have borne a large, thick horn on its forehead. Theories about the function of this horn include defence, attracting mates, driving away competitors, sweeping snow from the grass in winter and digging for water and plant roots. Like all rhinoceroses, elasmotheres were herbivorous. Unlike any others, its high-crowned molars were ever-growing. Its legs were longer than those of other rhinos and were adapted for galloping, giving it a horse-like gait. The known specimens of E. sibiricum reach up to 4.5 m (15 ft) in body length with shoulder heights over 2 m (6 ft 7 in). Elasmotherium weighed 4.5-5 ton.

Mapusaurus roseae
Mapusaurus ("Earth lizard") was a giant carnosaurian, Carcharodontosaurid dinosaur from the early Late Cretaceous (late Cenomanian to early Turonian stage) of what is now Argentina and possibly Chile. It was roughly similar in size to its close relative Giganotosaurus, averaging about 12.4 meters and 7 tons and getting to 13.6 meters long and 8.5 tons at maximum. The longest individual for which Coria and Currie (2006) provided a concrete estimate in Table 1 (apendix lll) is the animal to which femur MCF-PVPH-208.203 belonged; this individual is estimated as 10.2 metres (33 ft) long, but it is a juvenile. The fossil remains of Mapusaurus were discovered in a bone bed containing at least seven individuals of various growth stages. Coria and Currie speculated that this may represent a long term, possibly coincidental accumulation of carcasses (some sort of predator trap) and may provide clues about Mapusaurus behavior. Other known theropod bone beds include the Allosaurus-dominated Cleveland-Lloyd Dinosaur Quarry of Utah, an Albertosaurus bone bed from Alberta and a Daspletosaurus bone bed from Montana. Paleontologist Rodolfo Coria, of the Museo Carmen Funes, contrary to his published article, repeated in a press-conference earlier suggestions that this congregation of fossil bones may indicate that Mapusaurus hunted in groups and worked together to take down large prey, such as the immense sauropod Argentinosaurus. If so, this would be the first substantive evidence of gregarious behavior by large theropods other than Tyrannosaurus, although whether they might have hunted in organized packs (as wolves do) or simply attacked in a mob, is unknown.
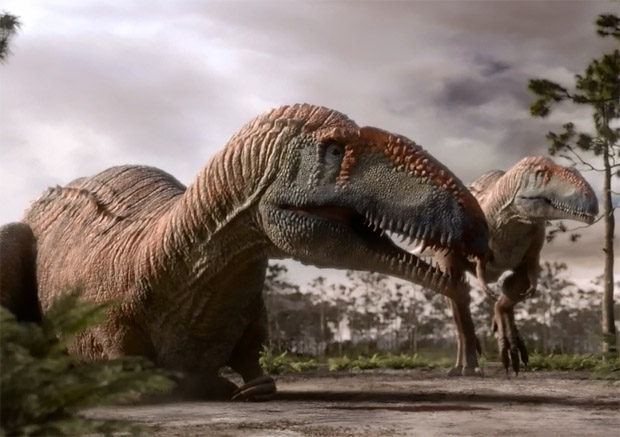
Credit to Wikipedia



