Post by dinosauria101 on May 23, 2019 16:18:20 GMT 5
Elasmotherium sibiricum
Elasmotherium ("thin plate beast") is an extinct genus of large rhinoceros endemic to Eurasia during the Late Pliocene through the Pleistocene, existing from 2.6 Ma to at least as late as 39,000 years ago in the Late Pleistocene. E. sibiricum, was the size of a mammoth and is thought to have borne a large, thick horn on its forehead. Theories about the function of this horn include defence, attracting mates, driving away competitors, sweeping snow from the grass in winter and digging for water and plant roots. Like all rhinoceroses, elasmotheres were herbivorous. Unlike any others, its high-crowned molars were ever-growing. Its legs were longer than those of other rhinos and were adapted for galloping, giving it a horse-like gait. The known specimens of E. sibiricum reach up to 4.5 m (15 ft) in body length with shoulder heights over 2 m (6 ft 7 in). Elasmotherium weighed 4.5-5 ton.

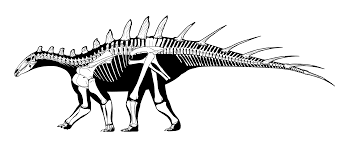
Dacentrurus armatus
Dacentrurus (meaning "tail full of points"), originally known as Omosaurus, was a large stegosaur of the Late Jurassic Period (154 - 150 mya) of Europe. Its type species, Omosaurus armatus, was named in 1875, based on a skeleton found in the Kimmeridge Clay of England. In 1902 the genus was renamed Dacentrurus because the name Omosaurus had already been used for a crocodylian. After 1875, half a dozen other species would be named but perhaps only Dacentrurus armatus is valid. Finds of this animal have been limited and much of its appearance is uncertain. It was a heavily built quadrupedal herbivore, adorned with plates and spikes. Dacentrurus was a large stegosaurid. Some specimens reached lengths 10 meters (33 ft) and weighed 8 t (8.8 short tons). Many books claim that Dacentrurus was a small stegosaur, when in fact finds such as a 1.5 metres (4.9 ft) wide pelvis indicate that Dacentrurus was among the largest of them. For a stegosaur the gut was especially broad, and a massive rump is also indicated by exceptionally wide dorsal vertebrae centra. The hindlimb was rather short, but the forelimb relatively long, largely because of a long lower arm. Although Dacentrurus is considered to have the same proportions as Stegosaurus, its plate and spike configuration is known to be rather different, as it probably had both two rows of small plates on its neck and two rows of longer spikes along its tail. The holotype specimen of Dacentrurus armatus contained a small blunt asymmetrical neck plate and also included a tail spike which could have been part of a thagomizer. The tail spike had sharp cutting edges on its front and rear side. Dacentrurus has sometimes been portrayed with a spike growing near the shoulder, similarly to a Kentrosaurus. Whether this portrayal is accurate or not is not yet determined.
Credit to Wikipedia
NOTE: I know the Dacentrurus is almost twice as big as its foe, but since most people favor similar sized opponents over stegosaurids (I'm unsure on that one), I gave the stegosaur a good deal of size advantage to potentially change the outcome
Elasmotherium ("thin plate beast") is an extinct genus of large rhinoceros endemic to Eurasia during the Late Pliocene through the Pleistocene, existing from 2.6 Ma to at least as late as 39,000 years ago in the Late Pleistocene. E. sibiricum, was the size of a mammoth and is thought to have borne a large, thick horn on its forehead. Theories about the function of this horn include defence, attracting mates, driving away competitors, sweeping snow from the grass in winter and digging for water and plant roots. Like all rhinoceroses, elasmotheres were herbivorous. Unlike any others, its high-crowned molars were ever-growing. Its legs were longer than those of other rhinos and were adapted for galloping, giving it a horse-like gait. The known specimens of E. sibiricum reach up to 4.5 m (15 ft) in body length with shoulder heights over 2 m (6 ft 7 in). Elasmotherium weighed 4.5-5 ton.

Dacentrurus armatus
Dacentrurus (meaning "tail full of points"), originally known as Omosaurus, was a large stegosaur of the Late Jurassic Period (154 - 150 mya) of Europe. Its type species, Omosaurus armatus, was named in 1875, based on a skeleton found in the Kimmeridge Clay of England. In 1902 the genus was renamed Dacentrurus because the name Omosaurus had already been used for a crocodylian. After 1875, half a dozen other species would be named but perhaps only Dacentrurus armatus is valid. Finds of this animal have been limited and much of its appearance is uncertain. It was a heavily built quadrupedal herbivore, adorned with plates and spikes. Dacentrurus was a large stegosaurid. Some specimens reached lengths 10 meters (33 ft) and weighed 8 t (8.8 short tons). Many books claim that Dacentrurus was a small stegosaur, when in fact finds such as a 1.5 metres (4.9 ft) wide pelvis indicate that Dacentrurus was among the largest of them. For a stegosaur the gut was especially broad, and a massive rump is also indicated by exceptionally wide dorsal vertebrae centra. The hindlimb was rather short, but the forelimb relatively long, largely because of a long lower arm. Although Dacentrurus is considered to have the same proportions as Stegosaurus, its plate and spike configuration is known to be rather different, as it probably had both two rows of small plates on its neck and two rows of longer spikes along its tail. The holotype specimen of Dacentrurus armatus contained a small blunt asymmetrical neck plate and also included a tail spike which could have been part of a thagomizer. The tail spike had sharp cutting edges on its front and rear side. Dacentrurus has sometimes been portrayed with a spike growing near the shoulder, similarly to a Kentrosaurus. Whether this portrayal is accurate or not is not yet determined.
Credit to Wikipedia
NOTE: I know the Dacentrurus is almost twice as big as its foe, but since most people favor similar sized opponents over stegosaurids (I'm unsure on that one), I gave the stegosaur a good deal of size advantage to potentially change the outcome




