Post by dinosauria101 on Jul 13, 2019 18:25:38 GMT 5
Euoplocephalus tutus
Euoplocephalus (play /juːˌɒplɵˈsɛfələs/ ew-op-lo-sef-ə-ləs; Greek: eu-/ευ- meaning 'well', hoplo-/οπλο- meaning 'armed' and kephale/κεφαλη meaning 'head', "well-armored head") was one of the largest genera of ankylosaurian dinosaurs, at about the size of a small elephant. It is also the ankylosaurian with the best fossil record, so its extensive spiked armor, low-slung body and great club-like tail are well documented. Among the ankylosaurids, Euoplocephalus was exceeded in size only by Tarchia and Ankylosaurus. Euoplocephalus was 6 metres (20 ft) long and weighed about 2.5 tonnes (2.8 short tons). It was also 2.4 metres (7.9 ft) wide. The head and body of Euoplocephalus were covered with bony armor, except for parts of the limbs and possibly the distal tail. Much of this armor was made up of small ossicles. Larger flat scutes, conical plates, and disc-shaped plates were arranged in transverse bands among this pavement of ossicles. Two bands protected the dorsal and lateral surfaces of the neck, four were present across the front part of the torso, three protected the pelvis, and four were present on the anterior half of the tail. The banded arrangement is thought to have permitted some freedom of movement.

Dacentrurus armatus
Dacentrurus (meaning "tail full of points"), originally known as Omosaurus, was a large stegosaur of the Late Jurassic Period (154 - 150 mya) of Europe. Its type species, Omosaurus armatus, was named in 1875, based on a skeleton found in the Kimmeridge Clay of England. In 1902 the genus was renamed Dacentrurus because the name Omosaurus had already been used for a crocodylian. After 1875, half a dozen other species would be named but perhaps only Dacentrurus armatus is valid. Finds of this animal have been limited and much of its appearance is uncertain. It was a heavily built quadrupedal herbivore, adorned with plates and spikes. Dacentrurus was a large stegosaurid. Some specimens reached lengths 10 meters (33 ft) and weighed 8 t (8.8 short tons). Many books claim that Dacentrurus was a small stegosaur, when in fact finds such as a 1.5 metres (4.9 ft) wide pelvis indicate that Dacentrurus was among the largest of them. For a stegosaur the gut was especially broad, and a massive rump is also indicated by exceptionally wide dorsal vertebrae centra. The hindlimb was rather short, but the forelimb relatively long, largely because of a long lower arm. Although Dacentrurus is considered to have the same proportions as Stegosaurus, its plate and spike configuration is known to be rather different, as it probably had both two rows of small plates on its neck and two rows of longer spikes along its tail. The holotype specimen of Dacentrurus armatus contained a small blunt asymmetrical neck plate and also included a tail spike which could have been part of a thagomizer. The tail spike had sharp cutting edges on its front and rear side. Dacentrurus has sometimes been portrayed with a spike growing near the shoulder, similarly to a Kentrosaurus. Whether this portrayal is accurate or not is not yet determined.
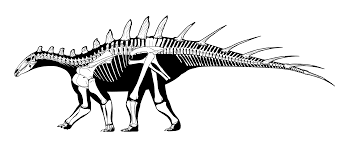
Credit to Wikipedia
NOTE: I know the Dacentrurus is over 3 times larger than the Euoplocephalus, but stegosaur weapons are extremely ill-equipped to deal with ankylosaurids, so I thought to give the stegosaur a good deal of size advantage to even the odds
Euoplocephalus (play /juːˌɒplɵˈsɛfələs/ ew-op-lo-sef-ə-ləs; Greek: eu-/ευ- meaning 'well', hoplo-/οπλο- meaning 'armed' and kephale/κεφαλη meaning 'head', "well-armored head") was one of the largest genera of ankylosaurian dinosaurs, at about the size of a small elephant. It is also the ankylosaurian with the best fossil record, so its extensive spiked armor, low-slung body and great club-like tail are well documented. Among the ankylosaurids, Euoplocephalus was exceeded in size only by Tarchia and Ankylosaurus. Euoplocephalus was 6 metres (20 ft) long and weighed about 2.5 tonnes (2.8 short tons). It was also 2.4 metres (7.9 ft) wide. The head and body of Euoplocephalus were covered with bony armor, except for parts of the limbs and possibly the distal tail. Much of this armor was made up of small ossicles. Larger flat scutes, conical plates, and disc-shaped plates were arranged in transverse bands among this pavement of ossicles. Two bands protected the dorsal and lateral surfaces of the neck, four were present across the front part of the torso, three protected the pelvis, and four were present on the anterior half of the tail. The banded arrangement is thought to have permitted some freedom of movement.

Dacentrurus armatus
Dacentrurus (meaning "tail full of points"), originally known as Omosaurus, was a large stegosaur of the Late Jurassic Period (154 - 150 mya) of Europe. Its type species, Omosaurus armatus, was named in 1875, based on a skeleton found in the Kimmeridge Clay of England. In 1902 the genus was renamed Dacentrurus because the name Omosaurus had already been used for a crocodylian. After 1875, half a dozen other species would be named but perhaps only Dacentrurus armatus is valid. Finds of this animal have been limited and much of its appearance is uncertain. It was a heavily built quadrupedal herbivore, adorned with plates and spikes. Dacentrurus was a large stegosaurid. Some specimens reached lengths 10 meters (33 ft) and weighed 8 t (8.8 short tons). Many books claim that Dacentrurus was a small stegosaur, when in fact finds such as a 1.5 metres (4.9 ft) wide pelvis indicate that Dacentrurus was among the largest of them. For a stegosaur the gut was especially broad, and a massive rump is also indicated by exceptionally wide dorsal vertebrae centra. The hindlimb was rather short, but the forelimb relatively long, largely because of a long lower arm. Although Dacentrurus is considered to have the same proportions as Stegosaurus, its plate and spike configuration is known to be rather different, as it probably had both two rows of small plates on its neck and two rows of longer spikes along its tail. The holotype specimen of Dacentrurus armatus contained a small blunt asymmetrical neck plate and also included a tail spike which could have been part of a thagomizer. The tail spike had sharp cutting edges on its front and rear side. Dacentrurus has sometimes been portrayed with a spike growing near the shoulder, similarly to a Kentrosaurus. Whether this portrayal is accurate or not is not yet determined.
Credit to Wikipedia
NOTE: I know the Dacentrurus is over 3 times larger than the Euoplocephalus, but stegosaur weapons are extremely ill-equipped to deal with ankylosaurids, so I thought to give the stegosaur a good deal of size advantage to even the odds






