Post by dinosauria101 on Jul 19, 2019 16:52:50 GMT 5
Sinotherium lagrelli
Sinotherium ("Chinese Beast") was a genus of single-horned rhinoceri of the late Miocene and Pliocene. It was ancestral to Elasmotherium, and its fossils have been found in western China. Sinotherium diverged from the ancestral genus, Iranotherium, first found in Iran, during the early Pliocene. Some experts prefer to lump Sinotherium, and Iranotherium into Elasmotherium.

Sauroniops pachytholus
Sauroniops was a large bipedal predator. The describers established several unique traits, differentiating Sauroniops from its relatives, such as Carcharodontosaurus which is found in the same layers. The nasal bone has an area of contact with the frontal bone over 40% of the latter's length. The frontal has in the left front corner a thick vaulted area. On the front upper rim the frontal has a trapezoid facet to contact the prefrontal, which is no part of the upper rim of the eye socket, and is separated from the facet for the lacrimal bone by a thin vertical ridge. The contact area with the lacrimal is D-shaped, extremely large and has four times the height of the facet with the postorbital bone. On the rear inner side of the frontal an elevated rim is present that is joint to the front vaulted area by a saddle-shaped depression and more towards the front midline of the skull continues in a series of rugosities. The frontal has a preserved length of 186 millimetres. Near the contact with the lacrimal the bone is extremely thickened to a height of seventy-three millimetres and vaulted; a second thick area is present at the rear separated from the first by a hollow surface. Such a thickening of the skull roof is more typical of the Abelisauridae in which group however, it is the postorbital that shows the phenomenon. The authors explained the thickening as an adaptation for display or to strengthen the skull for intraspecific head-butting.
Credit to Wikipedia
Sinotherium ("Chinese Beast") was a genus of single-horned rhinoceri of the late Miocene and Pliocene. It was ancestral to Elasmotherium, and its fossils have been found in western China. Sinotherium diverged from the ancestral genus, Iranotherium, first found in Iran, during the early Pliocene. Some experts prefer to lump Sinotherium, and Iranotherium into Elasmotherium.

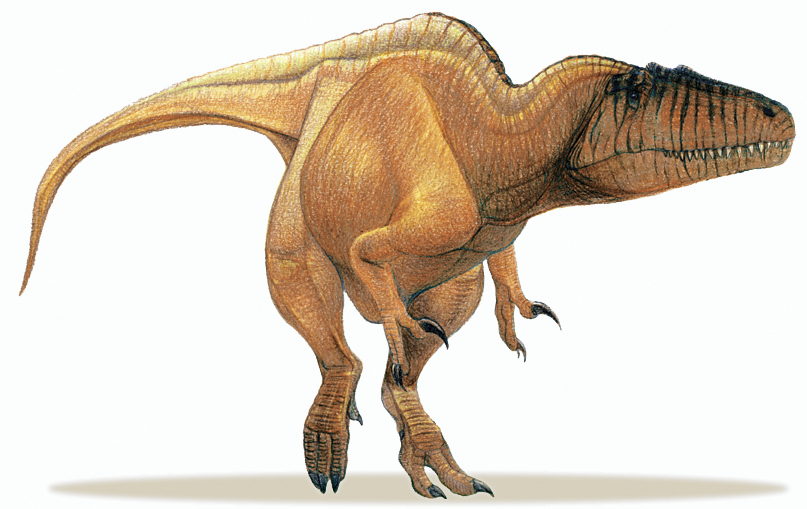
Sauroniops pachytholus
Sauroniops was a large bipedal predator. The describers established several unique traits, differentiating Sauroniops from its relatives, such as Carcharodontosaurus which is found in the same layers. The nasal bone has an area of contact with the frontal bone over 40% of the latter's length. The frontal has in the left front corner a thick vaulted area. On the front upper rim the frontal has a trapezoid facet to contact the prefrontal, which is no part of the upper rim of the eye socket, and is separated from the facet for the lacrimal bone by a thin vertical ridge. The contact area with the lacrimal is D-shaped, extremely large and has four times the height of the facet with the postorbital bone. On the rear inner side of the frontal an elevated rim is present that is joint to the front vaulted area by a saddle-shaped depression and more towards the front midline of the skull continues in a series of rugosities. The frontal has a preserved length of 186 millimetres. Near the contact with the lacrimal the bone is extremely thickened to a height of seventy-three millimetres and vaulted; a second thick area is present at the rear separated from the first by a hollow surface. Such a thickening of the skull roof is more typical of the Abelisauridae in which group however, it is the postorbital that shows the phenomenon. The authors explained the thickening as an adaptation for display or to strengthen the skull for intraspecific head-butting.

Credit to Wikipedia







