Post by dinosauria101 on Mar 13, 2019 9:02:35 GMT 5
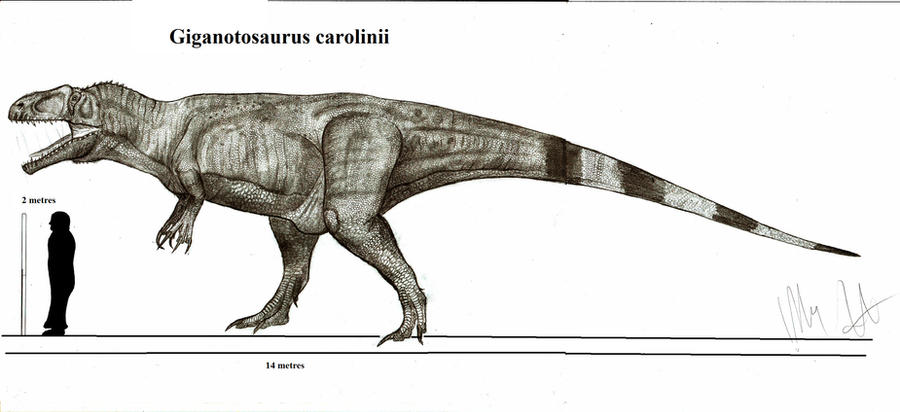
Giganotosaurus carolinii
Giganotosaurus ("giant southern lizard"), was a carcharodontosaurid dinosaur that lived 93 to 89 million years ago during the Turonian stage of the Late Cretaceous period. It is one of the longest known terrestrial carnivores, bigger than Tyrannosaurus, but in length and weight, smaller than Spinosaurus. Although longer than T. rex, G. carolinii was lighter and had a much smaller braincase that was the size and shape of a banana. A well-developed olfactory region means it probably had a good sense of smell. Titanosaur fossils have been recovered near the remains of Giganotosaurus, leading to speculation that these carnivores may have preyed on the giant herbivores. Fossils of related carcharodontosaurid fossils grouped closely together may indicate pack hunting, a behavior that could possibly extend to Giganotosaurus itself. he holotype specimen's (MUCPv-Ch1) skeleton was about 70% complete and included parts of the skull, a lower jaw, pelvis, hindlimbs and most of the backbone. The premaxillae, jugals, quadratojugals, the back of the lower jaws and the forelimbs are missing. Various estimates find that it measured somewhere between 12.2 and 13 m (40 and 43 ft) in length, and between 6.5 and 13.3 tons in weight. A second, more fragmentary, specimen (MUCPv-95) has also been identified, found in 1987 by Jorge Calvo. It is only known from the front part of the left dentary which is 8% larger than the equivalent bone from the holotype. This largest Giganotosaurus specimen is estimated to represent an individual with a skull length of 195 cm (6.40 ft), compared to the holotype's estimated at 1.80 m (5.9 ft) skull, making it likely that Giganotosaurus had the largest skull of any known theropod. Giganotosaurus surpassed Tyrannosaurus in mass by at least half a ton (the upper size estimate for T. rex is 9.1 t). Additionally several single teeth, discovered from 1987 onwards, have been referred to the species.
Tyrannotitan chubutensis
Tyrannotitan (meaning "titanic tyrant") is a genus of huge bipedal carnivorous dinosaur of the carcharodontosaurid family from the Aptian stage of the early Cretaceous period, discovered in Argentina. It is closely related to other giant predators like Carcharodontosaurus and especially Giganotosaurus as well as Mapusaurus. Tyrannotitan is the geologically oldest known giant carcharodontosaurid along with the more basal Acrocanthosaurus from North America (both found in Aptian-age rocks). Unlike other known carcharodontosaurids, this animal lacks pneumaticity extending into the sacral and caudal centra. The scapulocoracoid is fused, and much better developed than that of Giganotosaurus carolinii, yet the arm is very small. Most of the shaft of the scapula is missing. The length of these animals has been estimated at up to 11.4–12.2 metres (37–40 ft). In 2010, Gregory S. Paul gave higher estimations of 13 metres (43 ft). Its weight has been estimated between 4.9 and 7 tonnes (5.4 and 7.7 short tons).

Credit to Wikipedia
Giganotosaurus ("giant southern lizard"), was a carcharodontosaurid dinosaur that lived 93 to 89 million years ago during the Turonian stage of the Late Cretaceous period. It is one of the longest known terrestrial carnivores, bigger than Tyrannosaurus, but in length and weight, smaller than Spinosaurus. Although longer than T. rex, G. carolinii was lighter and had a much smaller braincase that was the size and shape of a banana. A well-developed olfactory region means it probably had a good sense of smell. Titanosaur fossils have been recovered near the remains of Giganotosaurus, leading to speculation that these carnivores may have preyed on the giant herbivores. Fossils of related carcharodontosaurid fossils grouped closely together may indicate pack hunting, a behavior that could possibly extend to Giganotosaurus itself. he holotype specimen's (MUCPv-Ch1) skeleton was about 70% complete and included parts of the skull, a lower jaw, pelvis, hindlimbs and most of the backbone. The premaxillae, jugals, quadratojugals, the back of the lower jaws and the forelimbs are missing. Various estimates find that it measured somewhere between 12.2 and 13 m (40 and 43 ft) in length, and between 6.5 and 13.3 tons in weight. A second, more fragmentary, specimen (MUCPv-95) has also been identified, found in 1987 by Jorge Calvo. It is only known from the front part of the left dentary which is 8% larger than the equivalent bone from the holotype. This largest Giganotosaurus specimen is estimated to represent an individual with a skull length of 195 cm (6.40 ft), compared to the holotype's estimated at 1.80 m (5.9 ft) skull, making it likely that Giganotosaurus had the largest skull of any known theropod. Giganotosaurus surpassed Tyrannosaurus in mass by at least half a ton (the upper size estimate for T. rex is 9.1 t). Additionally several single teeth, discovered from 1987 onwards, have been referred to the species.

Tyrannotitan chubutensis
Tyrannotitan (meaning "titanic tyrant") is a genus of huge bipedal carnivorous dinosaur of the carcharodontosaurid family from the Aptian stage of the early Cretaceous period, discovered in Argentina. It is closely related to other giant predators like Carcharodontosaurus and especially Giganotosaurus as well as Mapusaurus. Tyrannotitan is the geologically oldest known giant carcharodontosaurid along with the more basal Acrocanthosaurus from North America (both found in Aptian-age rocks). Unlike other known carcharodontosaurids, this animal lacks pneumaticity extending into the sacral and caudal centra. The scapulocoracoid is fused, and much better developed than that of Giganotosaurus carolinii, yet the arm is very small. Most of the shaft of the scapula is missing. The length of these animals has been estimated at up to 11.4–12.2 metres (37–40 ft). In 2010, Gregory S. Paul gave higher estimations of 13 metres (43 ft). Its weight has been estimated between 4.9 and 7 tonnes (5.4 and 7.7 short tons).

Credit to Wikipedia


