Post by dinosauria101 on Mar 18, 2019 20:51:12 GMT 5
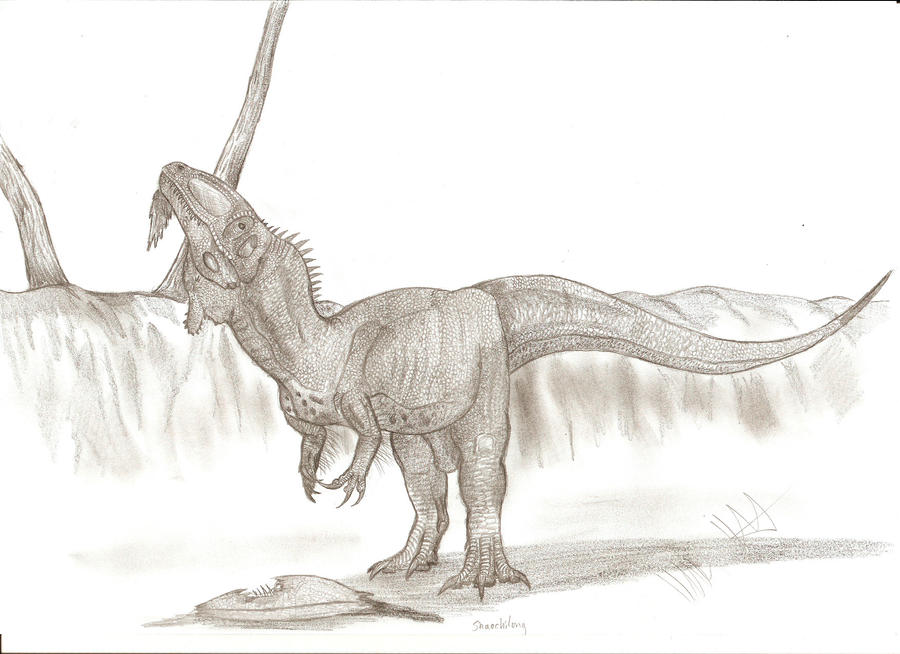
Shaochilong maortuensis

Temporal range: Late Cretaceous, 92 Ma
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Clade: Dinosauria
Clade: Theropoda
Family: †Carcharodontosauridae
Genus: †Shaochilong Brusatte et al., 2009
Shaochilong (meaning "shark toothed dragon") is a genus of carcharodontosaurid dinosaur from the mid Cretaceous (Turonian stage) Ulansuhai Formation of China (about 92 million years ago). The type species, S. maortuensis, was originally named Chilantaisaurus maortuensis, but was re-described and reclassified in 2009.
Discovery and subsequent analysis:
The holotype, IVPP V2885.1-7, consisting of skull fragments, axis and six caudal vertebrae associated to a single individual is the only known specimen. This specimen was discovered in Outer Mongolia and described by Hu in 1964 as a species of Chilantaisaurus. Chure (2002) and Rauhut (2001) suggested that it did not belong to that genus, and was probably a primitive coelurosaur. However, a re-description by Brusatte and colleagues in 2009 found that it was in fact a carcharodontosaurid, the first recognized from Asia. The genus was originally informally named "Alashansaurus".
IVPP V2885.1 was probably adult or nearly adult individual. Its length – based on the length of the maxillary tooth row – is estimated at 6 metres (20 ft). Estimated length of the femur is 61.5 cm, what suggests that whole animal weighted approximately 500 kilograms (1,100 lb).
Classification:
Phylogenetic analysis performed by Brusatte and coworkers indicate that Shaochilong is deeply nested within the carchorodontosaurids, the most derived group among the allosauroids. Surprisingly, Shaochilong appears to be more closely related to the Gondwanan carcharodontosaurids (Tyrannotitan, Carcharodontosaurus, Mapusaurus, Giganotosaurus) than the Laurasian ones (such as Neovenator and Acrocanthosaurus). Shaochilong is the youngest known Laurasian allosauroid suggesting that basal tetanurans not tyrannosaurids, were still the dominant group of large-bodied theropods in Laurasian during the Mid-Cretaceous and that the rise of tyrannosaurids as the dominant group of large terrestrial predators was sudden and confined to the very end of the Cretaceous.

Temporal range: Late Cretaceous, 92 Ma
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Clade: Dinosauria
Clade: Theropoda
Family: †Carcharodontosauridae
Genus: †Shaochilong Brusatte et al., 2009
Shaochilong (meaning "shark toothed dragon") is a genus of carcharodontosaurid dinosaur from the mid Cretaceous (Turonian stage) Ulansuhai Formation of China (about 92 million years ago). The type species, S. maortuensis, was originally named Chilantaisaurus maortuensis, but was re-described and reclassified in 2009.
Discovery and subsequent analysis:
The holotype, IVPP V2885.1-7, consisting of skull fragments, axis and six caudal vertebrae associated to a single individual is the only known specimen. This specimen was discovered in Outer Mongolia and described by Hu in 1964 as a species of Chilantaisaurus. Chure (2002) and Rauhut (2001) suggested that it did not belong to that genus, and was probably a primitive coelurosaur. However, a re-description by Brusatte and colleagues in 2009 found that it was in fact a carcharodontosaurid, the first recognized from Asia. The genus was originally informally named "Alashansaurus".
IVPP V2885.1 was probably adult or nearly adult individual. Its length – based on the length of the maxillary tooth row – is estimated at 6 metres (20 ft). Estimated length of the femur is 61.5 cm, what suggests that whole animal weighted approximately 500 kilograms (1,100 lb).
Classification:
Phylogenetic analysis performed by Brusatte and coworkers indicate that Shaochilong is deeply nested within the carchorodontosaurids, the most derived group among the allosauroids. Surprisingly, Shaochilong appears to be more closely related to the Gondwanan carcharodontosaurids (Tyrannotitan, Carcharodontosaurus, Mapusaurus, Giganotosaurus) than the Laurasian ones (such as Neovenator and Acrocanthosaurus). Shaochilong is the youngest known Laurasian allosauroid suggesting that basal tetanurans not tyrannosaurids, were still the dominant group of large-bodied theropods in Laurasian during the Mid-Cretaceous and that the rise of tyrannosaurids as the dominant group of large terrestrial predators was sudden and confined to the very end of the Cretaceous.



