Post by dinosauria101 on May 13, 2019 20:39:48 GMT 5
Quaesitosaurus orientalis
Quaesitosaurus (meaning "extraordinary lizard") is a genus of nemegtosaurid sauropod found by Kurzanov and Bannikov in 1983. The type species is Quaesitosaurus orientalis. It lived 70 million years ago during the Late Cretaceous. Its fossils, consisting solely of a partial skull, were found in Mongolia, and is estimated to have been about 26 metes (85 ft) based on its skull size. Long, low and horse-like with frontally located peg-teeth, it is similar enough to the skulls of Diplodocus and its kin to have prompted informed speculation that the missing body was formed like those of diplodocids. It is possible that Nemegtosaurus, also known from only skull material, is a very close relative of Quaesitosaurus.

Tarbosaurus bataar
Tarbosaurus belongs in the subfamily Tyrannosaurinae within the family Tyrannosauridae, along with the earlier Daspletosaurus, the more recent Tyrannosaurus and possibly Alioramus. Animals in this subfamily are more closely related to Tyrannosaurus than to Albertosaurus and are known for their robust build with proportionally larger skulls and longer femurs than in the other subfamily, the Albertosaurinae. Although many specimens of this genus have been found, little definite data was confirmed on the dinosaur as of 1986, though it was presumed to share many characteristics with other tyrannosaurids. The close similarities have prompted some scientists to suggest a possible link between the North American and Eurasian continents at that time, perhaps in the form of a land bridge.As with most dinosaurs, Tarbosaurus size estimates have varied through recent years. It could have been 10 to 12 meters long, with a weight of 5 - 7 tons.
Credit to Wikipedia
Quaesitosaurus (meaning "extraordinary lizard") is a genus of nemegtosaurid sauropod found by Kurzanov and Bannikov in 1983. The type species is Quaesitosaurus orientalis. It lived 70 million years ago during the Late Cretaceous. Its fossils, consisting solely of a partial skull, were found in Mongolia, and is estimated to have been about 26 metes (85 ft) based on its skull size. Long, low and horse-like with frontally located peg-teeth, it is similar enough to the skulls of Diplodocus and its kin to have prompted informed speculation that the missing body was formed like those of diplodocids. It is possible that Nemegtosaurus, also known from only skull material, is a very close relative of Quaesitosaurus.

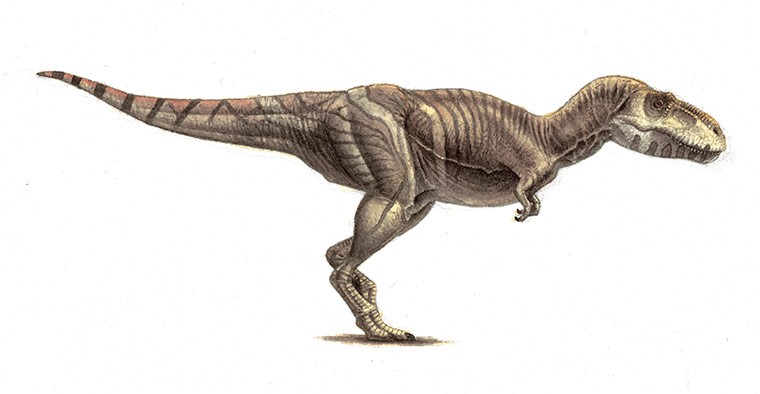
Tarbosaurus bataar
Tarbosaurus belongs in the subfamily Tyrannosaurinae within the family Tyrannosauridae, along with the earlier Daspletosaurus, the more recent Tyrannosaurus and possibly Alioramus. Animals in this subfamily are more closely related to Tyrannosaurus than to Albertosaurus and are known for their robust build with proportionally larger skulls and longer femurs than in the other subfamily, the Albertosaurinae. Although many specimens of this genus have been found, little definite data was confirmed on the dinosaur as of 1986, though it was presumed to share many characteristics with other tyrannosaurids. The close similarities have prompted some scientists to suggest a possible link between the North American and Eurasian continents at that time, perhaps in the form of a land bridge.As with most dinosaurs, Tarbosaurus size estimates have varied through recent years. It could have been 10 to 12 meters long, with a weight of 5 - 7 tons.

Credit to Wikipedia


