Post by dinosauria101 on Aug 16, 2019 17:11:45 GMT 5
Baryonyx walkeri
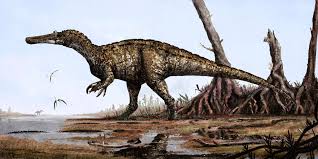
Baryonyx is a genus of theropod dinosaur which lived in the Barremian stage of the Early Cretaceous Period, about 130–125 million years ago. The first skeleton was discovered in 1983 in the Weald Clay Formation of Surrey, England, and became the holotype specimen of B. walkeri, named by palaeontologists Alan J. Charig and Angela C. Milner in 1986. The generic name, Baryonyx, means "heavy claw" and alludes to the animal's very large claw on the first finger; the specific name, walkeri, refers to its discoverer, amateur fossil collector William J. Walker. The holotype specimen is one of the most complete theropod skeletons from the UK (and remains the most complete spinosaurid), and its discovery attracted media attention. Specimens later discovered in other parts of the United Kingdom and Iberia have also been assigned to the genus. The holotype specimen, which may not have been fully grown, was estimated to have been between 7.5 and 10 m (25 and 33 ft) long and to have weighed between 1.2 and 1.7 t (1.3 and 1.9 short tons). Baryonyx had a long, low, and narrow snout, which has been compared to that of a gharial. The tip of the snout expanded to the sides in the shape of a rosette. Behind this, the upper jaw had a notch which fitted into the lower jaw (which curved upwards in the same area). It had a triangular crest on the top of its nasal bones. Baryonyx had a large number of finely serrated, conical teeth, with the largest teeth in front. The neck formed an S-shape, and the neural spines of its dorsal vertebrae increased in height from front to back. One elongated neural spine indicates it may have had a hump or ridge along the centre of its back. It had robust forelimbs, with the eponymous first-finger claw measuring about 31 cm (12 in) long. Baryonyx may have had semiaquatic habits, and coexisted with other theropod, ornithopod, and sauropod dinosaurs, as well as pterosaurs, crocodiles, turtles and fishes, in a fluvial environment.
Rajasaurus narmadensis
Rajasaurus was an abelisaurid, a member of a group of theropod predators known to have lived only on landmasses that were part of the supercontinent Gondwana, such as Africa, India, Madagascar, and South America. Rajasaurus closely resembles Majungasaurus, a contemporary abelisaur from Madagascar, an island that had separated from the Indian landmass about 20 million years earlier. It was found to be an abelisaurid through a phylogenetic analysis of anatomical characteristics, and was described as a carnotaurine abelisaurid (the subfamily including Carnotaurus) because of the configuration of its nasal bones and its possession of a growth ("excrescence") on its frontal bone. Rajasaurus is distinguished from other genera by its single nasal-frontal horn, the elongated proportions of its supratemporal fenestrae (holes in the upper rear of the skull), and the form of the ilia (principle bones of the hip) which feature a transverse ridge separating the brevis shelf from the hip joint. Rajasaurus was identified from a partial skeleton including a well–preserved skull (with a complete braincase and 70% of the rest of the skull bones recovered), hip bones and parts of the hind legs, backbone and tail. This specimen, GSI 21141/1–33, serves as the type specimen of the genus and species. Rajasaurus measured about 7.6–9 m (24.9–29.5 ft) long, 2.4 m (7.9 ft) in height, and weighed about 3 to 4 tons. The skull was short, measuring 60 cm (23.6 in) in length, and bore a distinctive low rounded horn. This horn is made up of outgrowths from the nasal and frontal bones.

Credit to Wikipedia
Baryonyx is a genus of theropod dinosaur which lived in the Barremian stage of the Early Cretaceous Period, about 130–125 million years ago. The first skeleton was discovered in 1983 in the Weald Clay Formation of Surrey, England, and became the holotype specimen of B. walkeri, named by palaeontologists Alan J. Charig and Angela C. Milner in 1986. The generic name, Baryonyx, means "heavy claw" and alludes to the animal's very large claw on the first finger; the specific name, walkeri, refers to its discoverer, amateur fossil collector William J. Walker. The holotype specimen is one of the most complete theropod skeletons from the UK (and remains the most complete spinosaurid), and its discovery attracted media attention. Specimens later discovered in other parts of the United Kingdom and Iberia have also been assigned to the genus. The holotype specimen, which may not have been fully grown, was estimated to have been between 7.5 and 10 m (25 and 33 ft) long and to have weighed between 1.2 and 1.7 t (1.3 and 1.9 short tons). Baryonyx had a long, low, and narrow snout, which has been compared to that of a gharial. The tip of the snout expanded to the sides in the shape of a rosette. Behind this, the upper jaw had a notch which fitted into the lower jaw (which curved upwards in the same area). It had a triangular crest on the top of its nasal bones. Baryonyx had a large number of finely serrated, conical teeth, with the largest teeth in front. The neck formed an S-shape, and the neural spines of its dorsal vertebrae increased in height from front to back. One elongated neural spine indicates it may have had a hump or ridge along the centre of its back. It had robust forelimbs, with the eponymous first-finger claw measuring about 31 cm (12 in) long. Baryonyx may have had semiaquatic habits, and coexisted with other theropod, ornithopod, and sauropod dinosaurs, as well as pterosaurs, crocodiles, turtles and fishes, in a fluvial environment.
Rajasaurus narmadensis
Rajasaurus was an abelisaurid, a member of a group of theropod predators known to have lived only on landmasses that were part of the supercontinent Gondwana, such as Africa, India, Madagascar, and South America. Rajasaurus closely resembles Majungasaurus, a contemporary abelisaur from Madagascar, an island that had separated from the Indian landmass about 20 million years earlier. It was found to be an abelisaurid through a phylogenetic analysis of anatomical characteristics, and was described as a carnotaurine abelisaurid (the subfamily including Carnotaurus) because of the configuration of its nasal bones and its possession of a growth ("excrescence") on its frontal bone. Rajasaurus is distinguished from other genera by its single nasal-frontal horn, the elongated proportions of its supratemporal fenestrae (holes in the upper rear of the skull), and the form of the ilia (principle bones of the hip) which feature a transverse ridge separating the brevis shelf from the hip joint. Rajasaurus was identified from a partial skeleton including a well–preserved skull (with a complete braincase and 70% of the rest of the skull bones recovered), hip bones and parts of the hind legs, backbone and tail. This specimen, GSI 21141/1–33, serves as the type specimen of the genus and species. Rajasaurus measured about 7.6–9 m (24.9–29.5 ft) long, 2.4 m (7.9 ft) in height, and weighed about 3 to 4 tons. The skull was short, measuring 60 cm (23.6 in) in length, and bore a distinctive low rounded horn. This horn is made up of outgrowths from the nasal and frontal bones.

Credit to Wikipedia


