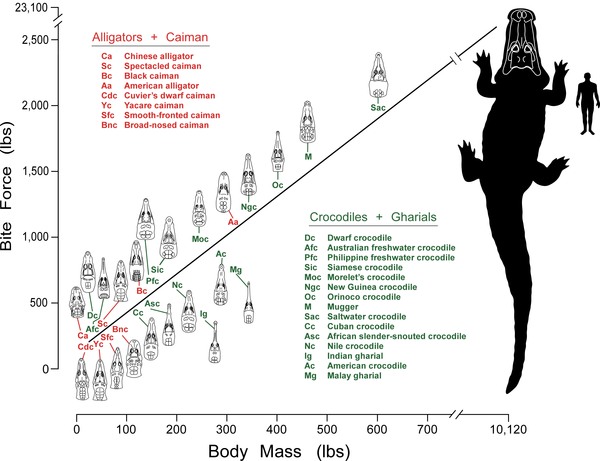
Post by DinosaurMichael on Sept 25, 2013 0:46:50 GMT 5
American Alligator - Alligator mississippiensis
The American alligator (Alligator mississippiensis), sometimes referred to colloquially as a gator, is a reptile endemic only to the Southeastern United States. It is one of the two living species of alligator, in the genus Alligator, within the family Alligatoridae. It is larger than the other extant alligator species, the Chinese alligator. The American alligator inhabits wetlands that frequently overlap with human-populated areas. The American alligator has a large, slightly rounded body, with thick limbs, a broad head, and a very powerful tail. Adult Alligators generally have dark gray or nearly black color. They may at times appear to be lighter based on detritus or algae in the water covering their skin. Juvenile alligators have a striped pattern for camouflage that they lose as they mature. Averaging about 9.5 in (24 cm) in length when newly hatched, alligators reach sexual maturity when they measure about 5–7 ft (1.5–2.1 m). Adult male alligators average 11.2 ft (3.4 m) in length, while adult females average 8.2 to 9.8 ft (2.5 to 3.0 m). Average adult body weights are reported from 270 to 800 lb (120 to 360 kg), with a few exceptionally large and old males exceeding 14 ft (4.3 m) and 1,000 pounds (450 kg). One American Alligator reached a length of 19 feet 2 inches (5.84 m) and 2,200 lb (1,000 kg), which made it not only the largest alligator ever recorded, but also among the largest crocodilians on record (although the related Black Caiman and 5 other crocodilians are believed to equal or exceed this size and prehistoric crocodilians such as Sarcosuchus, Deinosuchus, and Purussaurus reached much greater size). The tail, which accounts for half of the alligator's total length, is primarily used for aquatic propulsion. The tail can also be used as a weapon of defense when an alligator feels threatened. Alligators travel very quickly in water and while they are generally slow-moving on land, alligators can lunge short distances very quickly. They have five claws on each front foot and four on each rear foot. American Alligators have the strongest laboratory measured bite of any living animal, measured at up to 9,452 newtons (2,125 lbf) in laboratory conditions. It should be noted that this experiment has not (at the time of the paper published) been replicated in any other crocodilians.

Black Caiman - Melanosuchus niger
The black caiman, Melanosuchus niger, is a crocodilian. It is a carnivorous reptile that lives along slow-moving rivers and lakes, in the seasonally flooded savannas of the Amazon basin, and in other freshwater habitats in South America. Once common, it was hunted to near extinction primarily for its commercially valuable hide. It is now listed as Conservation Dependent. The black caiman has a bony ridge over brown eyes, and black, scaly skin. The skin coloration helps with camouflage during its nocturnal hunts, but may also help absorb heat (see thermoregulation). Mothers on guard near their nests are tormented by blood-sucking flies that gather around their vulnerable eyes leaving them bloodshot. Small black caiman can be distinguished from large spectacled caiman by their proportionately larger head and shorter tail, as well as by the color of the jaw, which is light colored in the spectacled caiman and dark with three black spots in the black caiman. The black caiman is one of the largest reptiles. It is the largest predator in the Amazon basin and possibly the largest member of the family Alligatoridae. Most adult black caimans are 3 to 4.26 metres (9.8–14 ft) in lengths, with old males rarely growing larger than 5 metres (16 ft). The black caiman broadly overlaps in size with the American alligator, although it is on average larger at maturity. In some areas (such as the Araguaia River) this species is consistently reported at 4 to 5 metres (13–16 ft) in length, much larger than the alligator (which rarely even reaches 4 meters), although specimens this size are uncommon. Several unconfirmed sources report that the black caiman can grow to 6 metres (20 ft) or more. It is, however, the third largest crocodilian in South America behind the American Crocodile and Orinoco Crocodile.

The American alligator (Alligator mississippiensis), sometimes referred to colloquially as a gator, is a reptile endemic only to the Southeastern United States. It is one of the two living species of alligator, in the genus Alligator, within the family Alligatoridae. It is larger than the other extant alligator species, the Chinese alligator. The American alligator inhabits wetlands that frequently overlap with human-populated areas. The American alligator has a large, slightly rounded body, with thick limbs, a broad head, and a very powerful tail. Adult Alligators generally have dark gray or nearly black color. They may at times appear to be lighter based on detritus or algae in the water covering their skin. Juvenile alligators have a striped pattern for camouflage that they lose as they mature. Averaging about 9.5 in (24 cm) in length when newly hatched, alligators reach sexual maturity when they measure about 5–7 ft (1.5–2.1 m). Adult male alligators average 11.2 ft (3.4 m) in length, while adult females average 8.2 to 9.8 ft (2.5 to 3.0 m). Average adult body weights are reported from 270 to 800 lb (120 to 360 kg), with a few exceptionally large and old males exceeding 14 ft (4.3 m) and 1,000 pounds (450 kg). One American Alligator reached a length of 19 feet 2 inches (5.84 m) and 2,200 lb (1,000 kg), which made it not only the largest alligator ever recorded, but also among the largest crocodilians on record (although the related Black Caiman and 5 other crocodilians are believed to equal or exceed this size and prehistoric crocodilians such as Sarcosuchus, Deinosuchus, and Purussaurus reached much greater size). The tail, which accounts for half of the alligator's total length, is primarily used for aquatic propulsion. The tail can also be used as a weapon of defense when an alligator feels threatened. Alligators travel very quickly in water and while they are generally slow-moving on land, alligators can lunge short distances very quickly. They have five claws on each front foot and four on each rear foot. American Alligators have the strongest laboratory measured bite of any living animal, measured at up to 9,452 newtons (2,125 lbf) in laboratory conditions. It should be noted that this experiment has not (at the time of the paper published) been replicated in any other crocodilians.
Black Caiman - Melanosuchus niger
The black caiman, Melanosuchus niger, is a crocodilian. It is a carnivorous reptile that lives along slow-moving rivers and lakes, in the seasonally flooded savannas of the Amazon basin, and in other freshwater habitats in South America. Once common, it was hunted to near extinction primarily for its commercially valuable hide. It is now listed as Conservation Dependent. The black caiman has a bony ridge over brown eyes, and black, scaly skin. The skin coloration helps with camouflage during its nocturnal hunts, but may also help absorb heat (see thermoregulation). Mothers on guard near their nests are tormented by blood-sucking flies that gather around their vulnerable eyes leaving them bloodshot. Small black caiman can be distinguished from large spectacled caiman by their proportionately larger head and shorter tail, as well as by the color of the jaw, which is light colored in the spectacled caiman and dark with three black spots in the black caiman. The black caiman is one of the largest reptiles. It is the largest predator in the Amazon basin and possibly the largest member of the family Alligatoridae. Most adult black caimans are 3 to 4.26 metres (9.8–14 ft) in lengths, with old males rarely growing larger than 5 metres (16 ft). The black caiman broadly overlaps in size with the American alligator, although it is on average larger at maturity. In some areas (such as the Araguaia River) this species is consistently reported at 4 to 5 metres (13–16 ft) in length, much larger than the alligator (which rarely even reaches 4 meters), although specimens this size are uncommon. Several unconfirmed sources report that the black caiman can grow to 6 metres (20 ft) or more. It is, however, the third largest crocodilian in South America behind the American Crocodile and Orinoco Crocodile.