Post by Carcharodon on Feb 9, 2014 10:14:58 GMT 5
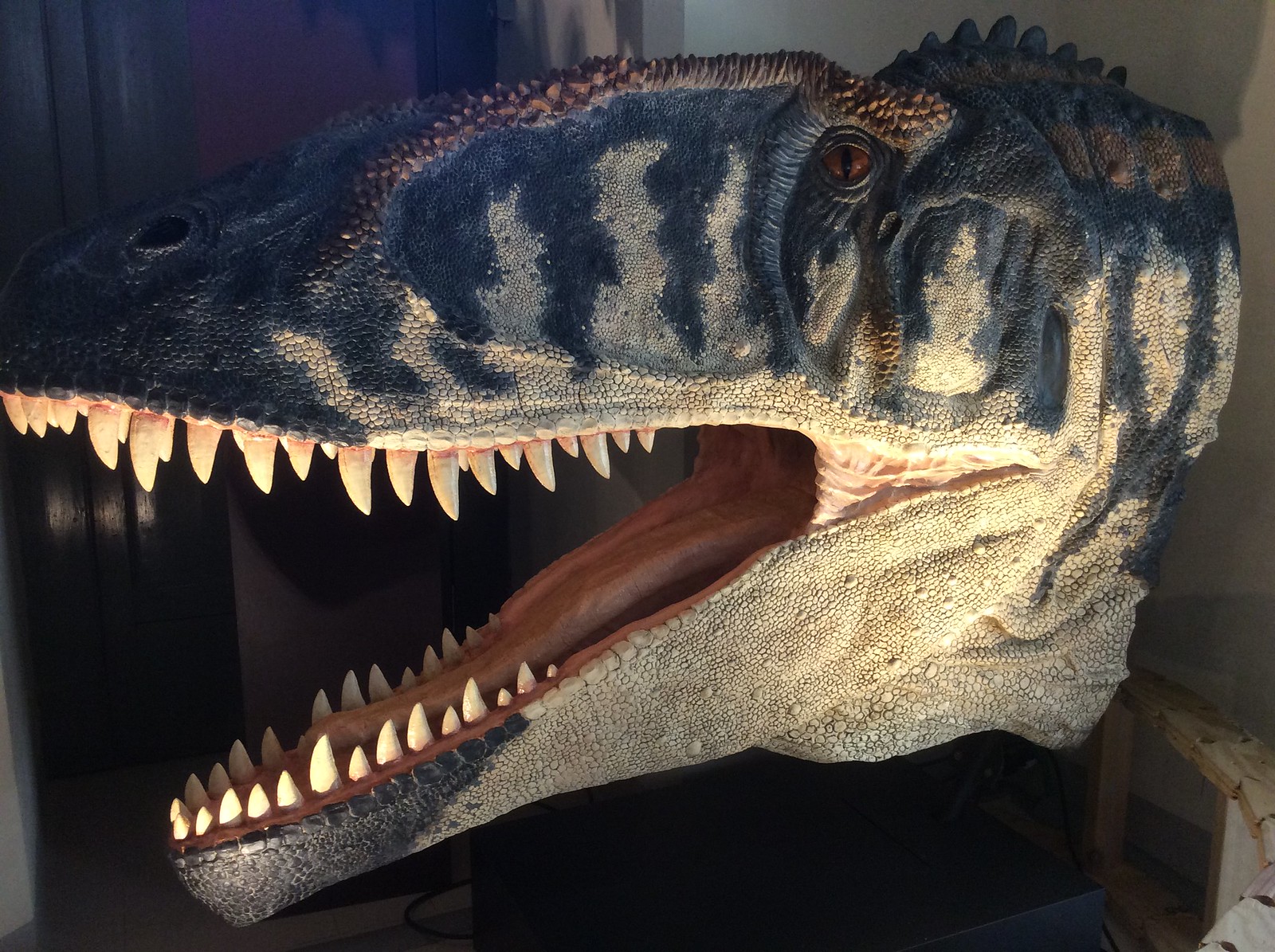
Concavenator corcovatus
Concavenator is a genus of theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 130 million years ago during the early Cretaceous period (Barremian stage). The type species is C. corcovatus; Concavenator corcovatus means "hump backed hunter from Cuenca". The fossil was discovered in the Las Hoyas fossil site of Spain by paleontologists José Luis Sanz, Francisco Ortega and Fernando Escaso from the Autonomous University of Madrid and the National University of Distance Learning. Concavenator was a medium-sized (roughly 6 meters (20 feet) long) primitive carcharodontosaurian dinosaur possessing several unique features. Two extremely tall vertebrae in front of the hips formed a tall but narrow and pointed crest (possibly supporting a hump) on the dinosaur's back. The function of such crests is currently unknown. Paleontologist Roger Benson from Cambridge University speculated that one possibility is that "it is analogous to head-crests used in visual displays", but the Spanish scientists who discovered it noted it could also be a thermal regulator. Additionally, the forelimb (ulna) of Concavenator preserved evidence of what may be quill knobs or homologous structures, an anatomical feature so far known only in animals with large, quilled feathers on the forelimb.

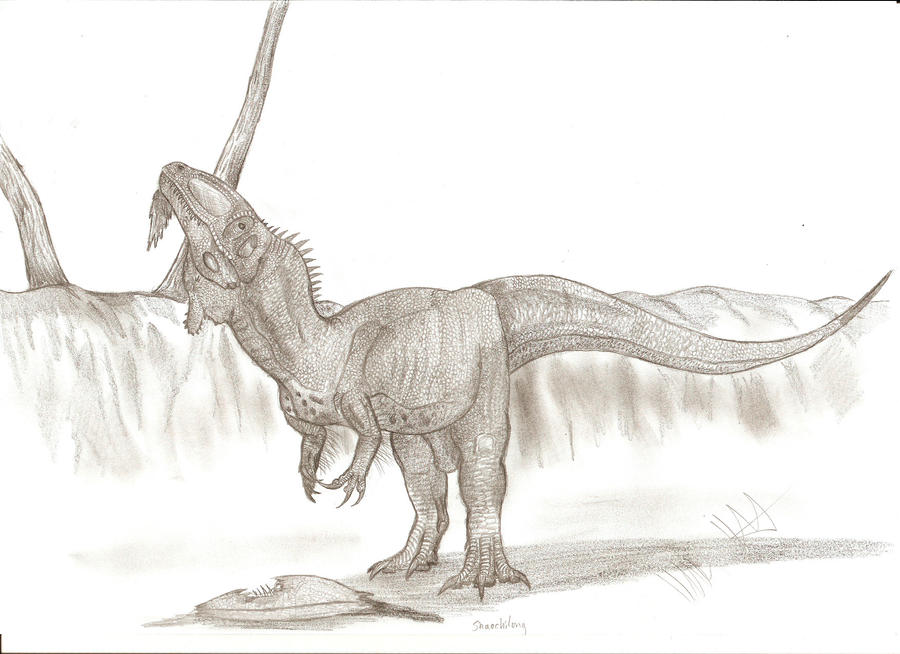
Shaochilong maortuensis
Shaochilong (meaning "shark toothed dragon") is a genus of carcharodontosaurid dinosaur from the mid Cretaceous (Turonian stage) Ulansuhai Formation of China (about 92 million years ago). The type species, S. maortuensis, was originally named Chilantaisaurus maortuensis, but was re-described and reclassified in 2009. The holotype, IVPP V2885.1-7, consisting of skull fragments, axis and six caudal vertebrae associated to a single individual is the only known specimen. This specimen was discovered in Outer Mongolia and described by Hu in 1964 as a species of Chilantaisaurus. Chure (2002) and Rauhut (2001) suggested that it did not belong to that genus, and was probably a primitive coelurosaur. However, a re-description by Brusatte and colleagues in 2009 found that it was in fact a carcharodontosaurid, the first recognized from Asia. The genus was originally informally named "Alashansaurus". Its length – based on the length of the maxillary tooth row – is estimated of 5 to 6 metres (16 to 20 ft). Estimated length of the femur is 61.5 cm, what suggests that whole animal weighted approximately 500 kilograms (1,100 lb).
Concavenator is a genus of theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 130 million years ago during the early Cretaceous period (Barremian stage). The type species is C. corcovatus; Concavenator corcovatus means "hump backed hunter from Cuenca". The fossil was discovered in the Las Hoyas fossil site of Spain by paleontologists José Luis Sanz, Francisco Ortega and Fernando Escaso from the Autonomous University of Madrid and the National University of Distance Learning. Concavenator was a medium-sized (roughly 6 meters (20 feet) long) primitive carcharodontosaurian dinosaur possessing several unique features. Two extremely tall vertebrae in front of the hips formed a tall but narrow and pointed crest (possibly supporting a hump) on the dinosaur's back. The function of such crests is currently unknown. Paleontologist Roger Benson from Cambridge University speculated that one possibility is that "it is analogous to head-crests used in visual displays", but the Spanish scientists who discovered it noted it could also be a thermal regulator. Additionally, the forelimb (ulna) of Concavenator preserved evidence of what may be quill knobs or homologous structures, an anatomical feature so far known only in animals with large, quilled feathers on the forelimb.

Shaochilong maortuensis
Shaochilong (meaning "shark toothed dragon") is a genus of carcharodontosaurid dinosaur from the mid Cretaceous (Turonian stage) Ulansuhai Formation of China (about 92 million years ago). The type species, S. maortuensis, was originally named Chilantaisaurus maortuensis, but was re-described and reclassified in 2009. The holotype, IVPP V2885.1-7, consisting of skull fragments, axis and six caudal vertebrae associated to a single individual is the only known specimen. This specimen was discovered in Outer Mongolia and described by Hu in 1964 as a species of Chilantaisaurus. Chure (2002) and Rauhut (2001) suggested that it did not belong to that genus, and was probably a primitive coelurosaur. However, a re-description by Brusatte and colleagues in 2009 found that it was in fact a carcharodontosaurid, the first recognized from Asia. The genus was originally informally named "Alashansaurus". Its length – based on the length of the maxillary tooth row – is estimated of 5 to 6 metres (16 to 20 ft). Estimated length of the femur is 61.5 cm, what suggests that whole animal weighted approximately 500 kilograms (1,100 lb).







