Post by Deleted on Nov 20, 2013 0:11:41 GMT 5
Ussuri Brown Bear - Ursus arctos lasiotus
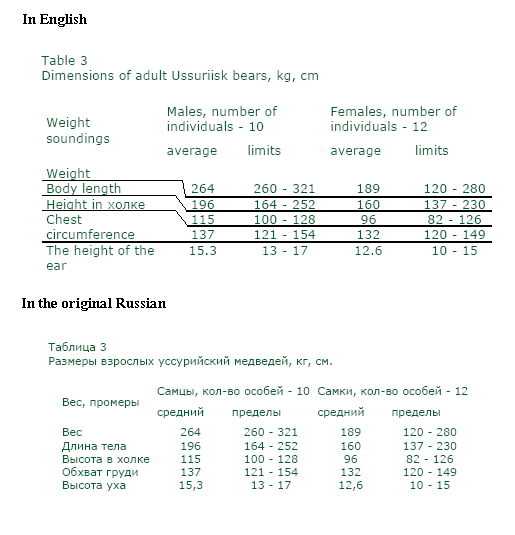
The Ussuri brown bear (Ursus arctos lasiotus), also known as the black grizzlyis a subspecies of the brown bear found in the Ussuri krai, Sakhalin, the Amur Oblast, northward to the Shantar Islands, Iturup Island, northeastern China, the Korean peninsula, Hokkaid? and Kunashiri Island. This subspecies is thought to be the ancestor of the North American grizzly bear. Ussuri brown bears crossed to Alaska 100,000 years ago, though they did not move south until 13,000 years ago. The Ainu people worshipped the Ussuri brown bear, eating its flesh and drinking its blood as part of a religious festival known as iomante. It is very similar to the Kamchatka brown bear, though it has a more elongated skull, a less elevated forehead, somewhat longer nasal bones and less separated zygomatic arches, and is somewhat darker in color, with some individuals being completely black, a fact which once led to the now refuted speculation that black individuals were hybrids of brown bears and Asian black bears. Adult males have skulls measuring 38.7 cm long and 23.5 cm wide. They can occasionally reach greater sizes than their Kamchatka counterparts: the largest skull measured by Sergej Ognew (1931) was only slightly smaller than that of the largest Alaskan bear on record at the time. In Sikhote Alin, Ussuri brown bears den mostly in burrows excavated into hillsides, though they will on rarer occasions den in rock outcroppings or build ground nests. These brown bears rarely encounter Asian black bears, as they den at higher elevations and on steeper slopes than the latter species. They may on rare occasions attack their smaller black cousins. In middle Sakhalin in spring, brown bears feed on the previous year's red bilberry, ants and flotsam, and at the end of the season, they concentrate on the shoots and rhizomes of tall grasses. On the southern part of the island, they feed primarily on flotsam, as well as insects and maple twigs. In springtime in Sikhote Alin, they feed on acorns, Manchurian walnuts and Korean nut pine seeds. In times of scarcity, in addition to bilberries and nuts, they capture larvae, wood-boring ants and lily roots. In early summer, they will strip bark from white-barked fir trees and feed on their cambium and sap. They will also eat berries from honeysuckle, yew, Amur grapevine and buckthorn. In southern Sakhalin, their summer diet consists of currents and chokeberries are eaten. In the August period in the middle part of the island, fish comprise 28% of their diet. In Hokkaido, the brown bear has a diet including small and large mammals, fish, birds and insects such as ants.

Siberian Tiger - Panthera tigris altacia
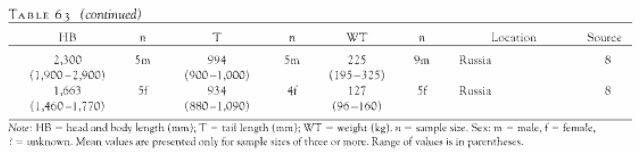
The Siberian tiger (Panthera tigris altaica), also known as the Amur tiger, is a tiger subspecies inhabiting mainly the Sikhote Alin mountain region with a small subpopulation in southwest Primorye province in the Russian Far East. In 2005, there were 331–393 adult-subadult Amur tigers in this region, with a breeding adult population of about 250 individuals. The population has been stable for more than a decade due to intensive conservation efforts, but partial surveys conducted after 2005 indicate that the Russian tiger population is declining. The Siberian tiger is the largest living felid and ranks among the biggest felids to ever exist. Results of a phylogeographic study comparing mitochondrial DNA from Caspian tigers and living tiger subspecies indicate that the common ancestor of the Amur and Caspian subspecies colonized Central Asia from eastern China via the Gansu?Silk Road corridor from eastern China, and then subsequently traversed Siberia eastward to establish the Amur tiger population in the Russian Far East. The Siberian tiger is reddish-rusty or rusty-yellow in color, with narrow black transverse stripes. The body length is not less than 150 cm (60 in), condylobasal length of skull 250 mm (10 in), zygomatic width 180 mm (7 in), and length of upper carnassial tooth over 26 mm (1 in) long. It has an extended supple body standing on rather short legs with a fairly long tail. It is typically 5–10 cm (2–4 in) taller than the Bengal tiger, which is about 107–110 cm (42–43 in) tall. Measurements taken by scientists of the Siberian Tiger Project in Sikhote-Alin range from 178 to 208 cm (70 to 82 in) in head and body length measured in straight line, with an average of 195 cm (77 in) for males; and for females ranging from 167 to 182 cm (66 to 72 in) with an average of 174 cm (69 in). The average tail measures 99 cm (39 in) in males and 91 cm (36 in) in females. The longest male "Maurice" measured 309 cm (122 in) in total length (tail of 101 cm (40 in)) and had a chest girth of 127 cm (50 in). The longest female "Maria Ivanna" measured 270 cm (110 in) in total length (tail of 88 cm (35 in)) and had a chest girth of 108 cm (43 in). These measurements show that the present Amur tiger is longer than the Bengal tiger and the African lion. According to modern research of wild Siberian tigers in Sikhote-Alin, an average adult male of more than 35 months of age weighs 176.4 kg (389 lb), the average asymptotic limit being 222.3 kg (490 lb); an adult tigress weighs 117.9 kg (260 lb). The mean weight of historical Siberian tigers is supposed to be higher: 215.3 kg (475 lb) for male tigers and 137.5 kg (303 lb) for females. In May 2011, a male called "Banzai" weighing 207 kg (456 lb) was radio-collared. This individual is heavier but smaller in size than a previously radio-collared male.

The Ussuri brown bear (Ursus arctos lasiotus), also known as the black grizzlyis a subspecies of the brown bear found in the Ussuri krai, Sakhalin, the Amur Oblast, northward to the Shantar Islands, Iturup Island, northeastern China, the Korean peninsula, Hokkaid? and Kunashiri Island. This subspecies is thought to be the ancestor of the North American grizzly bear. Ussuri brown bears crossed to Alaska 100,000 years ago, though they did not move south until 13,000 years ago. The Ainu people worshipped the Ussuri brown bear, eating its flesh and drinking its blood as part of a religious festival known as iomante. It is very similar to the Kamchatka brown bear, though it has a more elongated skull, a less elevated forehead, somewhat longer nasal bones and less separated zygomatic arches, and is somewhat darker in color, with some individuals being completely black, a fact which once led to the now refuted speculation that black individuals were hybrids of brown bears and Asian black bears. Adult males have skulls measuring 38.7 cm long and 23.5 cm wide. They can occasionally reach greater sizes than their Kamchatka counterparts: the largest skull measured by Sergej Ognew (1931) was only slightly smaller than that of the largest Alaskan bear on record at the time. In Sikhote Alin, Ussuri brown bears den mostly in burrows excavated into hillsides, though they will on rarer occasions den in rock outcroppings or build ground nests. These brown bears rarely encounter Asian black bears, as they den at higher elevations and on steeper slopes than the latter species. They may on rare occasions attack their smaller black cousins. In middle Sakhalin in spring, brown bears feed on the previous year's red bilberry, ants and flotsam, and at the end of the season, they concentrate on the shoots and rhizomes of tall grasses. On the southern part of the island, they feed primarily on flotsam, as well as insects and maple twigs. In springtime in Sikhote Alin, they feed on acorns, Manchurian walnuts and Korean nut pine seeds. In times of scarcity, in addition to bilberries and nuts, they capture larvae, wood-boring ants and lily roots. In early summer, they will strip bark from white-barked fir trees and feed on their cambium and sap. They will also eat berries from honeysuckle, yew, Amur grapevine and buckthorn. In southern Sakhalin, their summer diet consists of currents and chokeberries are eaten. In the August period in the middle part of the island, fish comprise 28% of their diet. In Hokkaido, the brown bear has a diet including small and large mammals, fish, birds and insects such as ants.

Siberian Tiger - Panthera tigris altacia
The Siberian tiger (Panthera tigris altaica), also known as the Amur tiger, is a tiger subspecies inhabiting mainly the Sikhote Alin mountain region with a small subpopulation in southwest Primorye province in the Russian Far East. In 2005, there were 331–393 adult-subadult Amur tigers in this region, with a breeding adult population of about 250 individuals. The population has been stable for more than a decade due to intensive conservation efforts, but partial surveys conducted after 2005 indicate that the Russian tiger population is declining. The Siberian tiger is the largest living felid and ranks among the biggest felids to ever exist. Results of a phylogeographic study comparing mitochondrial DNA from Caspian tigers and living tiger subspecies indicate that the common ancestor of the Amur and Caspian subspecies colonized Central Asia from eastern China via the Gansu?Silk Road corridor from eastern China, and then subsequently traversed Siberia eastward to establish the Amur tiger population in the Russian Far East. The Siberian tiger is reddish-rusty or rusty-yellow in color, with narrow black transverse stripes. The body length is not less than 150 cm (60 in), condylobasal length of skull 250 mm (10 in), zygomatic width 180 mm (7 in), and length of upper carnassial tooth over 26 mm (1 in) long. It has an extended supple body standing on rather short legs with a fairly long tail. It is typically 5–10 cm (2–4 in) taller than the Bengal tiger, which is about 107–110 cm (42–43 in) tall. Measurements taken by scientists of the Siberian Tiger Project in Sikhote-Alin range from 178 to 208 cm (70 to 82 in) in head and body length measured in straight line, with an average of 195 cm (77 in) for males; and for females ranging from 167 to 182 cm (66 to 72 in) with an average of 174 cm (69 in). The average tail measures 99 cm (39 in) in males and 91 cm (36 in) in females. The longest male "Maurice" measured 309 cm (122 in) in total length (tail of 101 cm (40 in)) and had a chest girth of 127 cm (50 in). The longest female "Maria Ivanna" measured 270 cm (110 in) in total length (tail of 88 cm (35 in)) and had a chest girth of 108 cm (43 in). These measurements show that the present Amur tiger is longer than the Bengal tiger and the African lion. According to modern research of wild Siberian tigers in Sikhote-Alin, an average adult male of more than 35 months of age weighs 176.4 kg (389 lb), the average asymptotic limit being 222.3 kg (490 lb); an adult tigress weighs 117.9 kg (260 lb). The mean weight of historical Siberian tigers is supposed to be higher: 215.3 kg (475 lb) for male tigers and 137.5 kg (303 lb) for females. In May 2011, a male called "Banzai" weighing 207 kg (456 lb) was radio-collared. This individual is heavier but smaller in size than a previously radio-collared male.